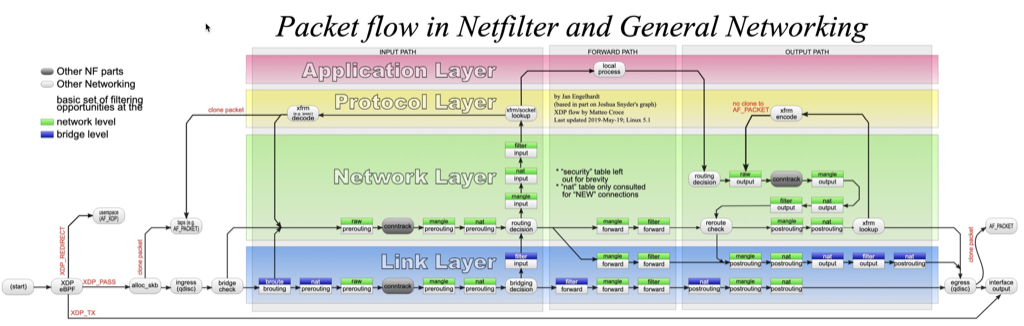
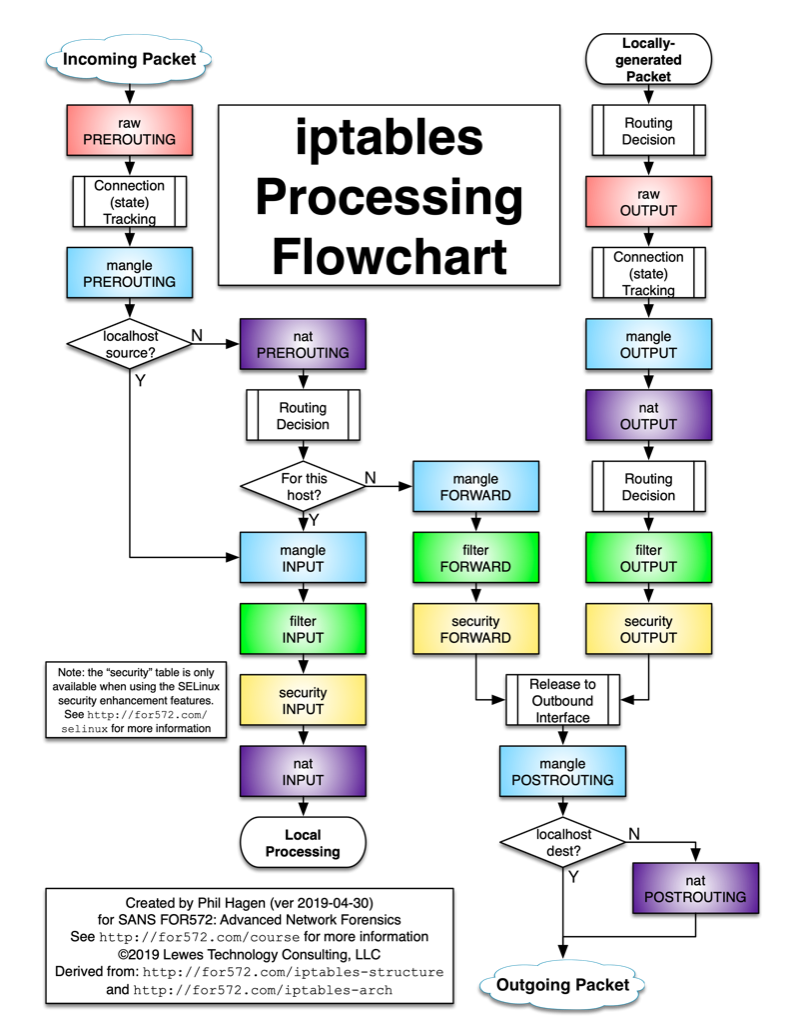
iptables使用 结构
包流
iptables监控reset的连接信息 如果连接被reset需要记录下reset包是哪边发出来的,并记录reset连接的四元组信息
iptables规则 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Wed Apr 1 11:39:31 2020 *filter :INPUT ACCEPT [557:88127] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [527:171711] # 不监听3406上的reset,日志前面添加 [plantegg] -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp ! --sport 3406 --tcp-flags RST RST -j LOG --log-prefix "[plantegg] " --log-level 7 --log-tcp-sequence --log-tcp-options --log-ip-options # -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp ! --dport 3406 --tcp-flags RST RST -j LOG --log-prefix "[plantegg] " --log-level7 --log-tcp-sequence --log-tcp-options --log-ip-options -A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp ! --sport 3406 --tcp-flags RST RST -j LOG --log-prefix "[plantegg] " --log-level 7 --log-tcp-sequence --log-tcp-options --log-ip-options COMMIT # Completed on Wed Apr 1 11:39:31 2020
将如上配置保存在 plantegg_filter.conf中,设置开机启动:
1 2 3 //注意,tee 命令的 "-a" 选项的作用等同于 ">>" 命令,如果去除该选项,那么 tee 命令的作用就等同于 ">" 命令。 //echo -1 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/perf_event_paranoid //sudo强行修改写入 echo "sudo iptables-restore < plantegg_filter.conf" | sudo tee -a /etc/rc.d/rc.local
单独记录到日志文件中 默认情况下 iptables 日志记录在 dmesg中不方便查询,可以修改rsyslog.d规则将日志存到单独的文件中:
1 2 # cat /etc/rsyslog.d/plantegg_filter_log.conf :msg, startswith, "[plantegg]" -/home/admin/logs/plantegg-tcp.log
将 [plantegg] 开头的日志存到对应的文件
将如上配置放到: /etc/rsyslog.d/ 目录下, 重启 rsyslog 就生效了
1 2 3 sudo cp /home/admin/plantegg-worker/install/plantegg_filter_log.conf /etc/rsyslog.d/plantegg_filter_log.conf sudo chown -R root:root /etc/rsyslog.d/plantegg_filter_log.conf sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
防止日志打满磁盘 配置 logrotate, 保留最近30天的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 # cat /etc/logrotate.d/drds/home/admin/logs/drds-tcp.log { daily rotate 30 copytruncate compress dateext # size 1k prerotate /usr/bin/chattr -a /home/admin/logs/drds-tcp.log endscript postrotate /usr/bin/chattr +a /home/admin/logs/drds-tcp.log endscript } 执行: sudo /usr/sbin/logrotate --force --verbose /etc/logrotate.d/drds debug: sudo /usr/sbin/logrotate -d --verbose /etc/logrotate.d/drds 查看日志: cat /var/lib/logrotate/logrotate.status
logrotate操作的日志需要权限正常,并且上级目录权限也要对,解决方案参考:https://chasemp.github.io/2013/07/24/su-directive-logrotate/ 报错信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 rotating pattern: /var/log/myapp/*.log weekly (4 rotations) empty log files are rotated, old logs are removed considering log /var/log/myapp/default.log error: skipping "/var/log/myapp/default.log" because parent directory has insecure permissions (It's world writable or writable by group which is not "root") Set "su" directive in config file to tell logrotate which user/group should be used for rotation
最终效果 1 2 3 4 5 $tail -10 logs/drds-tcp.log Apr 26 15:27:36 vb kernel: [drds] IN= OUT=eth0 SRC=10.0.186.75 DST=10.0.175.109 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=64 ID=0 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=8182 DPT=9366 SEQ=0 ACK=1747027778 WINDOW=0 RES=0x00 ACK RST URGP=0 Apr 26 15:27:36 vb kernel: [drds] IN= OUT=eth0 SRC=10.0.186.75 DST=10.0.175.109 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=64 ID=0 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=8182 DPT=9368 SEQ=0 ACK=3840170438 WINDOW=0 RES=0x00 ACK RST URGP=0 Apr 26 15:27:36 vb kernel: [drds] IN= OUT=eth0 SRC=10.0.186.75 DST=10.0.175.109 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=64 ID=0 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=8182 DPT=9370 SEQ=0 ACK=3892381139 WINDOW=0 RES=0x00 ACK RST URGP=0 Apr 26 15:27:38 vb kernel: [drds] IN= OUT=eth0 SRC=10.0.186.75 DST=10.0.171.173 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=64 ID=0 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=8182 DPT=38225 SEQ=0 ACK=1436910913 WINDOW=0 RES=0x00 ACK RST URGP=0
tracing_point 监控 对于 4.19内核的kernel,可以通过tracing point来监控重传以及reset包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 # grep tcp:tcp /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/available_events tcp:tcp_probe tcp:tcp_retransmit_synack tcp:tcp_rcv_space_adjust tcp:tcp_destroy_sock tcp:tcp_receive_reset tcp:tcp_send_reset tcp:tcp_retransmit_skb //开启本机发出的 reset 监控,默认输出到:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_pipe # echo 1 > /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/tcp/tcp_send_reset/enable//如下是开启重传以及reset的记录,本机ip 10.0.186.140 # cat trace_pipe//重传 <idle>-0 [002] ..s. 9520196.657431: tcp_retransmit_skb: sport=3306 dport=62460 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 Wisp-Root-Worke-540 [000] .... 9522308.074233: tcp_destroy_sock: sport=3306 dport=20594 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 sock_cookie=51a C2 CompilerThre-543 [002] ..s. 9522308.074296: tcp_destroy_sock: sport=3306 dport=20670 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 sock_cookie=574 // 被reset Wisp-Root-Worke-540 [002] ..s. 9522519.353756: tcp_receive_reset: sport=33822 dport=8080 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.193 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.193 sock_cookie=5dd // 主动reset DragoonAgent-28297 [002] .... 9522433.144611: tcp_send_reset: sport=8182 dport=61783 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.174 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.174 Wisp-Root-Worke-540 [002] ..s. 9522519.353773: tcp_send_reset: sport=33822 dport=8080 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.193 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.193 // 3306对端中断 cat-28727 [000] ..s. 9524341.650740: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=3306 dport=23262 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 oldstate=TCP_SYN_RECV newstate=TCP_ESTABLISHED <idle>-0 [000] .ns. 9524397.184608: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=3306 dport=23262 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 oldstate=TCP_ESTABLISHED newstate=TCP_CLOSE //8182 主动关闭 <idle>-0 [000] .Ns. 9525499.045236: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=8182 dport=25448 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.174 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.174 oldstate=TCP_SYN_RECV newstate=TCP_ESTABLISHED DragoonAgent-6240 [001] .... 9525499.118092: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=8182 dport=25448 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.174 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.174 oldstate=TCP_ESTABLISHED newstate=TCP_FIN_WAIT1 <idle>-0 [000] ..s. 9525499.159032: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=8182 dport=25448 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.174 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.174 oldstate=TCP_FIN_WAIT1 newstate=TCP_FIN_WAIT2 <idle>-0 [000] .Ns. 9525499.159056: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=8182 dport=25448 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.171.174 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.171.174 oldstate=TCP_FIN_WAIT2 newstate=TCP_CLOSE //3306 被动关闭 <idle>-0 [002] .Ns. 9524484.864509: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=3306 dport=23360 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 oldstate=TCP_SYN_RECV newstate=TCP_ESTABLISHED cat-28568 [002] ..s. 9524496.913199: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=3306 dport=23360 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 oldstate=TCP_ESTABLISHED newstate=TCP_CLOSE_WAIT Wisp-Root-Worke-540 [003] .... 9524496.915450: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=3306 dport=23360 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 oldstate=TCP_CLOSE_WAIT newstate=TCP_LAST_ACK Wisp-Root-Worke-539 [002] .Ns. 9524496.915572: inet_sock_set_state: family=AF_INET protocol=IPPROTO_TCP sport=3306 dport=23360 saddr=10.0.186.140 daddr=10.0.186.70 saddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.140 daddrv6=::ffff:10.0.186.70 oldstate=TCP_LAST_ACK newstate=TCP_CLOSE
iptables 打通网络 1 2 //本机到 172.16.0.102 不通,但是和 47.100.29.16能通(阿里云弹性ip) iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -d 172.16.0.102 -j DNAT --to-destination 47.100.29.16
ipset 组合iptables使用 ipset是iptables的扩展,它允许创建匹配地址集合的规则。普通的iptables链只能单IP匹配, 进行规则匹配时,是从规则列表中从头到尾一条一条进行匹配,这像是在链表中搜索指定节点费力。ipset 提供了把这个 O(n) 的操作变成 O(1) 的方法:就是把要处理的 IP 放进一个集合,对这个集合设置一条 iptables 规则。像 iptable 一样,IP sets 是 Linux 内核提供,ipset 这个命令是对它进行操作的一个工具。
ipset 可以以set的形式管理大批IP以及IP段,set可以有多个,通过 ipset修改set后可以立即生效。不用再次修改iptables规则。k8s也会用ipset来管理ip集合
ipset is an extension to iptables that allows you to create firewall rules that match entire “sets” of addresses at once. Unlike normal iptables chains, which are stored and traversed linearly, IP sets are stored in indexed data structures, making lookups very efficient, even when dealing with large sets.
接下来用一个ip+port的白名单案例来展示他们的用法,ipset负责白名单,iptables负责拦截规则:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 240 [2021-11-30 19:57:10] ipset list drds_whitelist_ips |grep "^127.0." 241 [2021-11-30 19:57:27] ipset del drds_whitelist_ips 127.0.0.1 //从set删除ip 248 [2021-11-30 19:58:50] ipset list drds_whitelist_ips |grep "^11.1.2" 249 [2021-11-30 19:59:05] ipset del drds_whitelist_ips 11.1.2.30 # timeout 259200是集合内新增的IP有三天的寿命ipset create myset hash:net timeout 259200 ipset list drds_whitelist_ips //列出set中的所有ip、ip段 ipset add drds_whitelist_ips 100.1.2.0/24 //从set中增加ip段 iptables -I INPUT 1 -p tcp -j drds_whitelist //创建新规则链drds_whitelist,所有tcp流入的包都跳转到 drds_whitelist规则 //有了以上drds_whitelist_ips这个名单, 接下来可以在iptables规则中使用这个set了 //在第一行增加规则:访问端口1234的tcp请求走规则 drds_whitelist iptables -I INPUT 1 -p tcp --dport 1234 -j drds_whitelist //规则drds_whitelist 添加如下三条 //第一条白名单中的来源ip访问1234就ACCEPT,不再走后面的. 关键的白名单列表就取自ipset中的drds_whitelist_ips iptables -A drds_whitelist -m set --match-set drds_whitelist_ips src -p tcp --dport 1234 -j ACCEPT //同规则1,记录日志,走到这里说明规则1没生效,那么就是黑名单要拦截的了 iptables -A drds_whitelist -p tcp --dport 1234 -j LOG --log-prefix '[drds_reject] ' --log-level 7 --log-tcp-sequence --log-tcp-options --log-ip-options //拦截 iptables -A drds_whitelist -p tcp --dport 1234 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
经过如上操作后,可以得到iptables规则如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 # iptables -L -n --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination drds_whitelist tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:1234 Chain drds_whitelist (1 references) target prot opt source destination 1 ACCEPT tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 match-set drds_whitelist_ips src tcp dpt:80 2 LOG tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:1234 LOG flags 7 level 7 prefix `[drds_reject] ` --log-level 7 --log-tcp-sequence --log-tcp-options --log-ip-options ' 3 REJECT tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:1234 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
从以上Chain drds_whitelist中删除第三条规则
1 iptables -D drds_whitelist 3
block ip 案例 模拟断网测试的时候可以通过iptables固定屏蔽某几个ip来实现。
创建ipset,存放好需要block的ip列表
1 2 ipset create block_ips hash:net timeout 259200 ipset add block_ips 10.176.2.245
添加iptables过滤规则,规则中不需要列出一堆ip,只需要指定上一步创建好的ipset,以后屏蔽、放开某些ip不需要修改iptables规则了,只需要往ipset添加、删除目标ip
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 iptables -N drds_rule //创建新规则链 iptables -I INPUT 1 -m set --match-set block_ips src -p tcp -j drds_rule //命中就跳转到drds_rule //这条可有可无,记录日志,方便调试 iptables -I drds_rule -m set --match-set block_ips src -j LOG --log-prefix '[drds_reject] ' --log-level 7 --log-tcp-sequence --log-tcp-options --log-ip-options iptables -A drds_rule -m set --match-set block_ips src -p tcp -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
iptables记录日志 记录每个新连接创建的时间,日志在/var/log/kern或者/var/log/dmesg中:
1 2 3 4 5 iptables -I INPUT -m state --state NEW -j LOG --log-prefix "Connection In: " iptables -I OUTPUT -m state --state NEW -j LOG --log-prefix "Connection Out: " //检查包,记录invalid包到日志中 iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate INVALID -m limit --limit 1/sec -j LOG --log-prefix "invalid: " --log-level 7
在宿主机上执行,然后在dmesg中能看到包的传递流程。只有raw有TRACE能力,nat、filter、mangle都没有。这个方式对性能影响非常大,时延高(增加1秒左右)
1 2 iptables -t raw -A OUTPUT -p icmp -j TRACE iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p icmp -j TRACE
iptables 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 10.176.7.5 -p tcp --dport 8507 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.176.7.6:3307 iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 18080 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.176.7.245:8080 # 将访问8022端口的进出流量转发到22端口 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 8022 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 22 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 8507 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 3307 # 将本机的端口转发到其他机器 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.172.130 -p tcp --dport 8000 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.172.131:80 # 将192.168.172.131:80 端口将数据返回给客户端时,将源ip改为192.168.172.130 iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -d 192.168.172.131 -p tcp --dport 80 -j SNAT --to 192.168.172.130 # ip 转发,做完转发后netstat能看到两条连接 sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -d 100.69.170.27 -j DNAT --to-destination 127.0.0.1 /sbin/iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -d 23.27.6.15 -j DNAT --to-destination 45.61.255.176 /sbin/iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -d 45.61.255.176 -j SNAT --to-source 23.27.6.15 /sbin/iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s 45.61.255.176 -j SNAT --to-source 23.27.6.15 # 清空nat表的所有链 iptables -t nat -F PREROUTING # 禁止访问某个端口 iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 31165 -j DROP
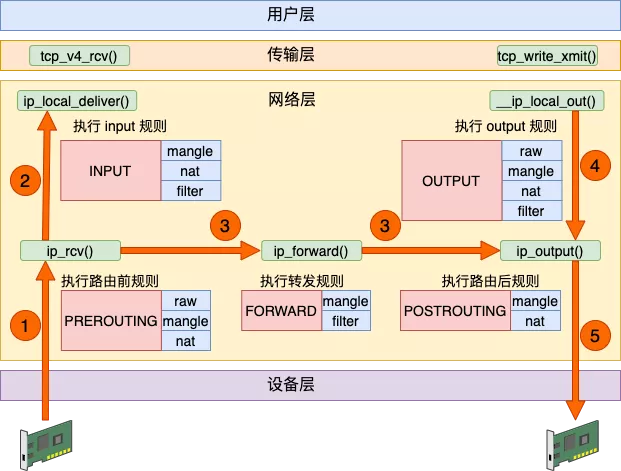
iptables 工作图如下,进来的包走1、2;出去的包走4、5;转发的包走1、3、5
ncat端口转发 1 2 监听本机 9876 端口,将数据转发到 192.168.172.131的 80 端口 ncat --sh-exec "ncat 192.168.172.131 80" -l 9876 --keep-open
scat
1 2 在本地监听12345端口,并将请求转发至192.168.172.131的22端口。 socat TCP4-LISTEN:12345,reuseaddr,fork TCP4:192.168.172.131:22
iptables 屏蔽IP 一分钟内新建22端口连接超过 4 次,不分密码对错, 直接 block.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name SSH --rsource iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --seconds 60 --hitcount 4 --name SSH --rsource -j DROP 或者 block 掉暴力破解 ssh 的 IP grep "Failed" /var/log/auth.log | \ awk '{print $(NF-3)}' | \ sort | uniq -c | sort -n | \ awk '{if ($1>100) print $2}' | \ xargs -I {} iptables -A INPUT -s {} -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --sport 3306 -j DROP iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 3306 -j DROP
Per-IP rate limiting with iptables
iptables 扔掉指定端口的 ack 包 1 2 //扔掉发给 8000 端口的 ack 包,但是不要扔 rst包 sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 8000 -m tcp ! --tcp-flags RST,ACK RST,ACK -m tcp --tcp-flags ACK ACK -j DROP
将 ack delay 1 秒中,故意制造乱序:
1 2 3 4 5 6 tc qdisc add dev eth0 root handle 1: prio tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:3 handle 30: netem delay 1000ms iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 8000 -m tcp ! --tcp-flags RST,ACK RST,ACK -m tcp --tcp-flags ACK ACK -j MARK --set-mark 3 tc filter add dev eth0 protocol ip parent 1:0 prio 3 handle 3 fw flowid 1:3
执行效果(在 172.26.137.120.17922 端抓包):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 15:31:57.815944 IP 172.26.137.120.17922 > 172.26.137.130.8000: Flags [S], seq 2408440162, win 29200, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 1952321086 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0 15:31:57.815963 IP 172.26.137.130.8000 > 172.26.137.120.17922: Flags [S.], seq 1188559140, ack 2408440163, win 65160, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 1076070423 ecr 1952321086,nop,wscale 7], length 0 15:31:57.816236 IP 172.26.137.120.17922 > 172.26.137.130.8000: Flags [R.], seq 1, ack 1, win 229, options [nop,nop,TS val 1952321086 ecr 1076070423], length 0 //本来是先 ack,再 RST,但因为 ack delay 了导致先抓到 RST //1 秒后 ack 发出 15:31:58.816225 IP 172.26.137.120.17922 > 172.26.137.130.8000: Flags [.], ack 1, win 229, options [nop,nop,TS val 1952321086 ecr 1076070423], length 0 15:31:58.816264 IP 172.26.137.130.8000 > 172.26.137.120.17922: Flags [R], seq 1188559141, win 0, length 0
iptables 常用参数
-I : Insert rule at given rule number
-t : Specifies the packet matching table such as nat, filter, security, mangle, and raw.
-L : List info for specific chain (such as INPUT/FORWARD/OUTPUT) of given packet matching table
–line-numbers : See firewall rules with line numbers
-n : Do not resolve names using dns i.e. only show numeric output for IP address and port numbers.
-v : Verbose output. This option makes the list command show the interface name, the rule options (if any), and the TOS masks
NetFilter Hooks 下面几个 hook 是内核协议栈中已经定义好的:
NF_IP_PRE_ROUTING: 接收到的包进入协议栈后立即触发此 hook,在进行任何路由判断 (将包发往哪里)之前NF_IP_LOCAL_IN: 接收到的包经过路由判断,如果目的是本机,将触发此 hookNF_IP_FORWARD: 接收到的包经过路由判断,如果目的是其他机器,将触发此 hookNF_IP_LOCAL_OUT: 本机产生的准备发送的包,在进入协议栈后立即触发此 hookNF_IP_POST_ROUTING: 本机产生的准备发送的包或者转发的包,在经过路由判断之后, 将触发此 hook
IPTables 表和链(Tables and Chains) 下面可以看出,内置的 chain 名字和 netfilter hook 名字是一一对应的:
PREROUTING: 由 NF_IP_PRE_ROUTING hook 触发INPUT: 由 NF_IP_LOCAL_IN hook 触发FORWARD: 由 NF_IP_FORWARD hook 触发OUTPUT: 由 NF_IP_LOCAL_OUT hook 触发POSTROUTING: 由 NF_IP_POST_ROUTING hook 触发
如果没有匹配到任何规则那么执行默认规则。下面括号中的policy
1 2 3 4 #iptables -L | grep policy Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
If you would rather deny all connections and manually specify which ones you want to allow to connect, you should change the default policy of your chains to drop. Doing this would probably only be useful for servers that contain sensitive information and only ever have the same IP addresses connect to them.
1 2 3 iptables --policy INPUT DROP` `iptables --policy OUTPUT DROP` `iptables --policy FORWARD DROP
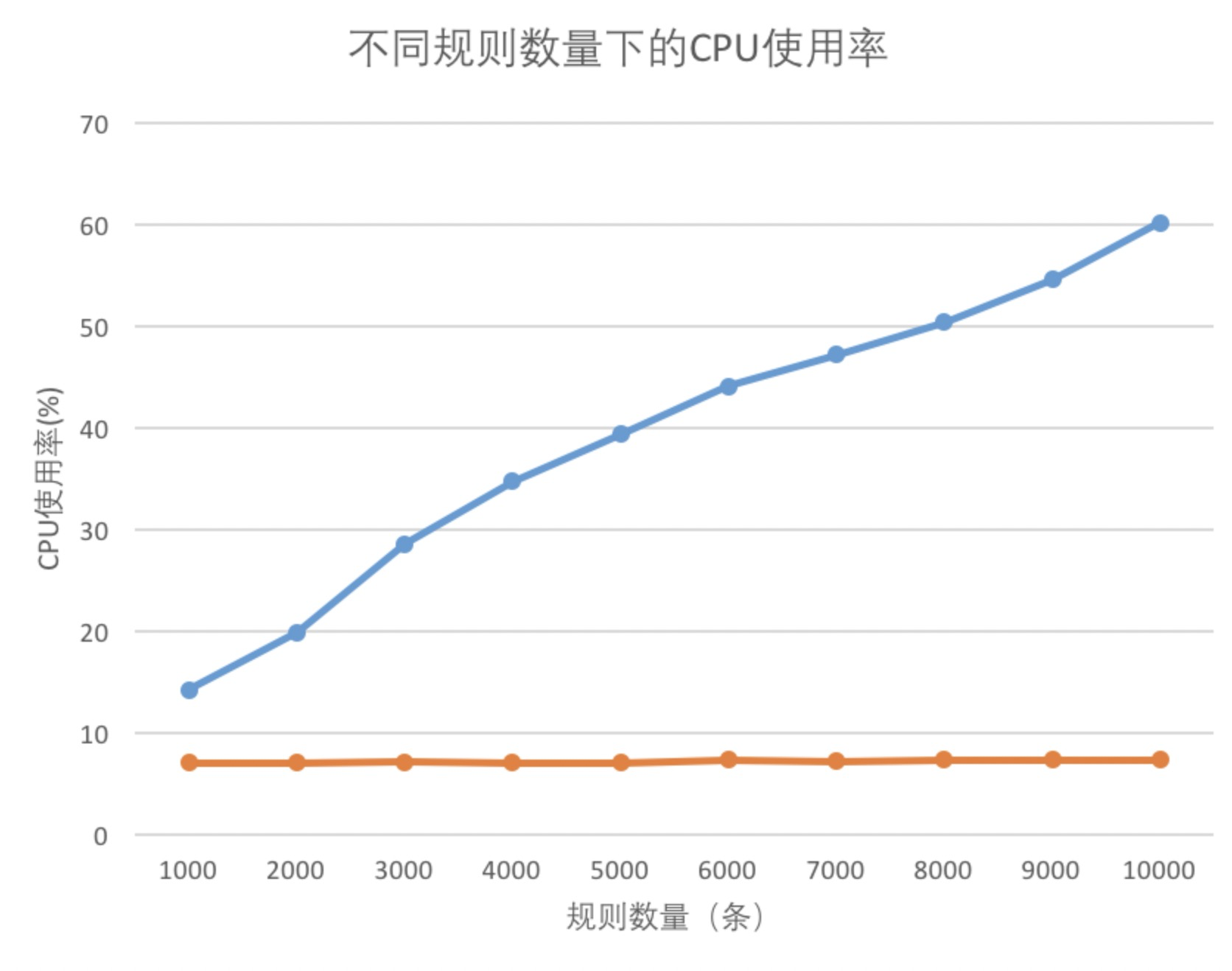
iptables规则对性能的影响 蓝色是iptables规则数量,不过如果规则内容差不多,只是ip不一样,完全可以用ipset将他们合并到一条或者几条规则,从而提升性能
iptables 丢包监控 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 //每 2 秒中 diff 一下因为命中 iptables 导致的 Drop 包的数量,并高亮差异(丢包数), -v :Verbose output watch -d "iptables -nvL | grep DROP " //输出如下: Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 19G packets, 3618G bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 15 600 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:8000 option=!8 flags:0x04/0x04 160 6400 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22345 option=!8 flags:0x04/0x04
参考资料 深入理解 iptables 和 netfilter 架构
NAT - 网络地址转换(2016)
通过iptables 来控制每个ip的流量
iptables 实用教程