kubernetes Flannel网络剖析
kubernetes Flannel网络剖析
cni(Container Network Interface)
CNI 全称为 Container Network Interface,是用来定义容器网络的一个 规范。containernetworking/cni 是一个 CNCF 的 CNI 实现项目,包括基本的 bridge,macvlan等基本网络插件。
一般将cni各种网络插件的可执行文件二进制放到 /usr/libexec/cni/ ,在 /etc/cni/net.d/ 下创建配置文件,剩下的就交给 K8s 或者 containerd 了,我们不关心也不了解其实现。
比如:
1 | # ls -lh /usr/libexec/cni/ |
CNI 插件都是直接通过 exec 的方式调用,而不是通过 socket 这样 C/S 方式,所有参数都是通过环境变量、标准输入输出来实现的。
跨主机通信流程
Step-by-step communication from Pod 1 to Pod 6:
- Package leaves *Pod 1 netns* through the *eth1* interface and reaches the root netns* through the virtual interface veth1*;
- Package leaves veth1* and reaches cni0*, looking for Pod 6*’s* address;
- Package leaves cni0* and is redirected to eth0*;
- Package leaves *eth0* from Master 1* and reaches the gateway*;
- Package leaves the *gateway* and reaches the *root netns* through the eth0* interface on Worker 1*;
- Package leaves eth0* and reaches cni0*, looking for Pod 6*’s* address;
- Package leaves *cni0* and is redirected to the *veth6* virtual interface;
- Package leaves the *root netns* through *veth6* and reaches the *Pod 6 netns* though the *eth6* interface;
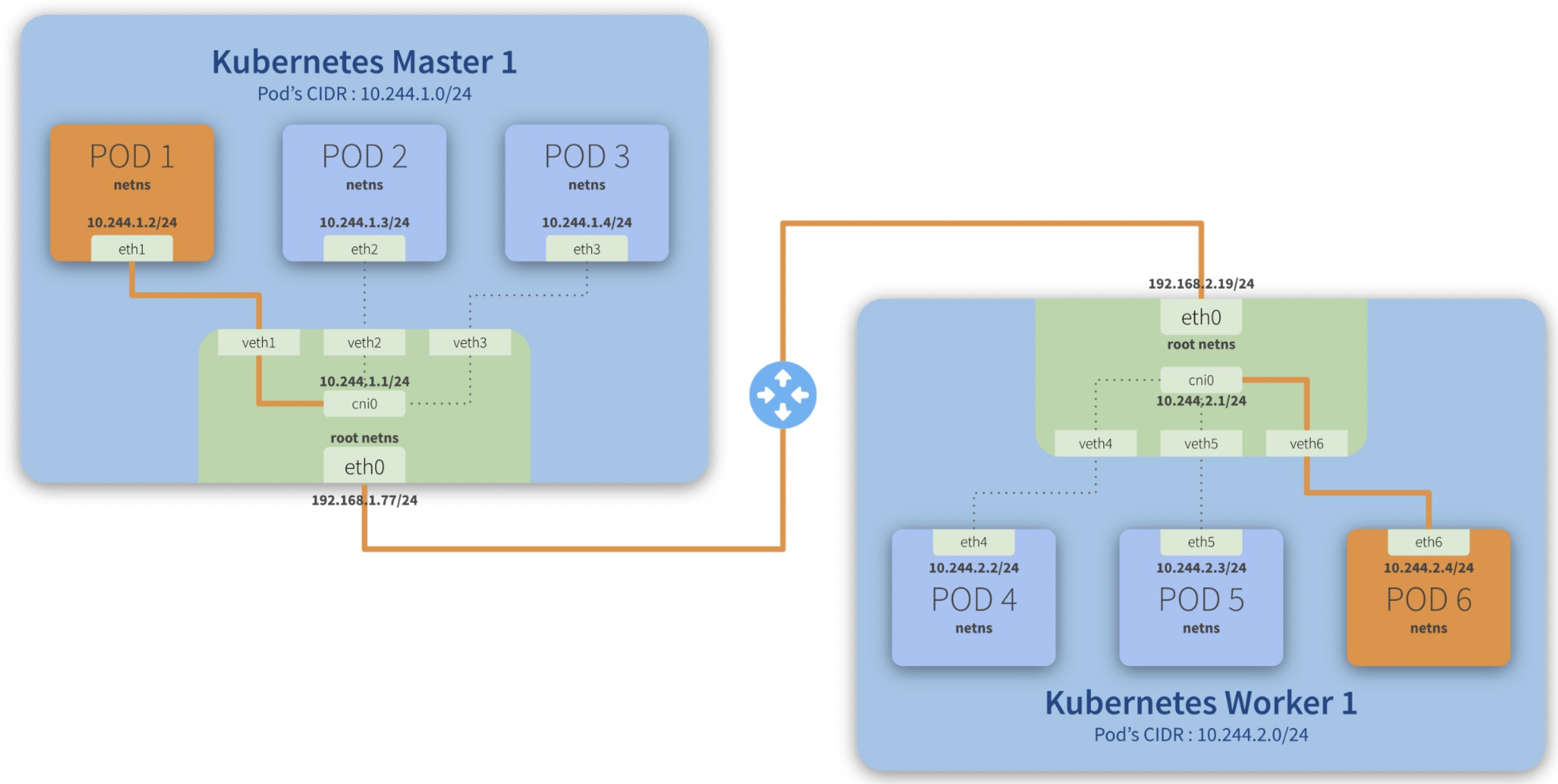
cni0 is a Linux network bridge device, all veth devices will connect to this bridge, so all Pods on the same node can communicate with each other, as explained in Kubernetes Network Model and the hotel analogy above.
默认cni 网络是没法跨宿主机的,跨宿主机需要走overlay(比如flannel的vxlan)或者仅限宿主机全在一个二层网络可达(比如用flannel的host-gw模式)
flannel vxlan网络
什么是 flannel
Flannel is a simple and easy way to configure a layer 3 network fabric designed for Kubernetes.
Flannel 工作原理
Flannel runs a small, single binary agent called
flanneldon each host, and is responsible for allocating a subnet lease to each host out of a larger, preconfigured address space. Flannel uses either the Kubernetes API or etcd directly to store the network configuration, the allocated subnets, and any auxiliary data (such as the host’s public IP). Packets are forwarded using one of several backend mechanisms including VXLAN and various cloud integrations.
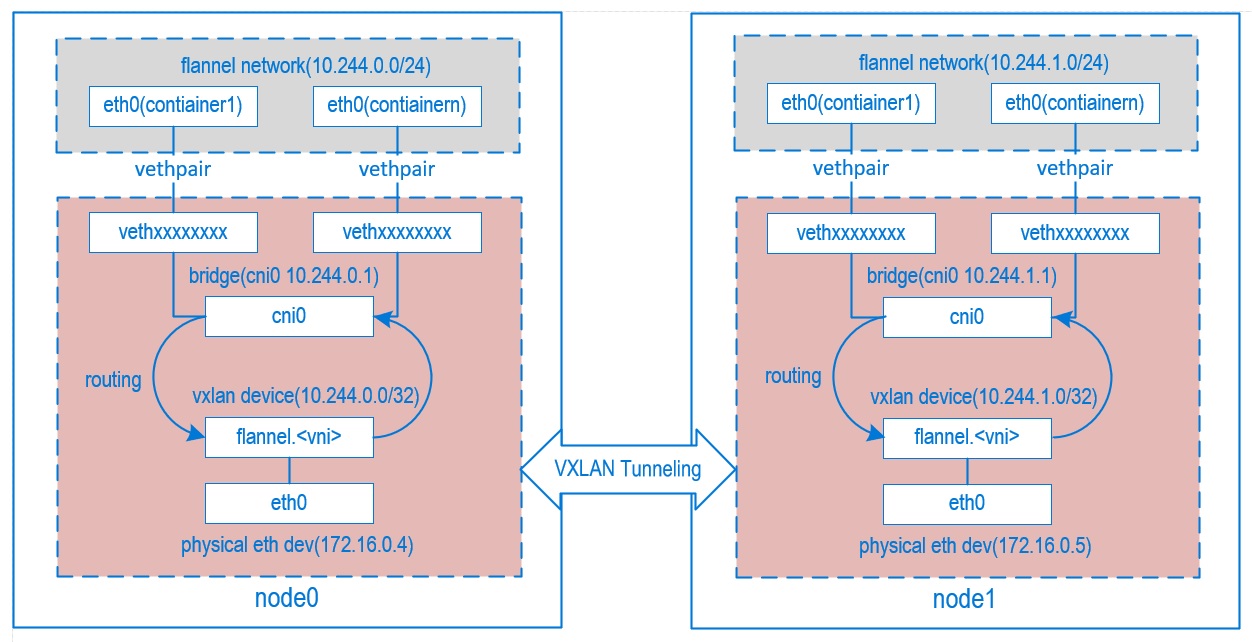
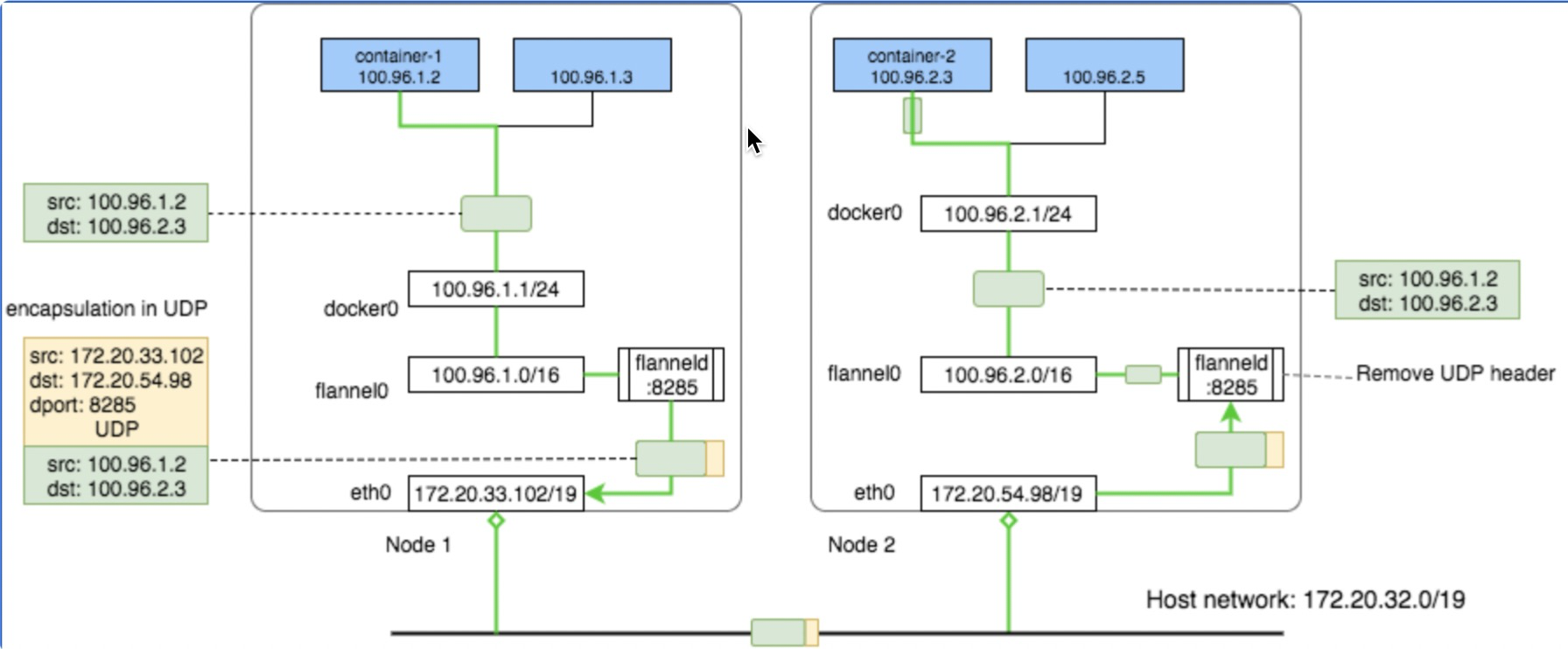
核心原理就是将pod网络包通过vxlan协议封装成一个udp包,udp包的ip是数据ip,内层是pod原始网络通信包。
假如POD1访问POD4:
- 从POD1中出来的包先到Bridge cni0上(因为POD1对应的veth挂在了cni0上),目标mac地址是cni0的Mac
- 然后进入到宿主机网络,宿主机有路由 10.244.2.0/24 via 10.244.2.0 dev flannel.1 onlink ,也就是目标ip 10.244.2.3的包交由 flannel.1 来处理,目标mac地址是POD4所在机器的flannel.1的Mac
- flanneld 进程将包封装成vxlan 丢到eth0从宿主机1离开(封装后的目标ip是192.168.2.91,现在都是由内核来完成flanneld这个封包过程,性能好)
- 这个封装后的vxlan udp包正确路由到宿主机2
- 然后经由 flanneld 解包成 10.244.2.3 ,命中宿主机2上的路由:10.244.2.0/24 dev cni0 proto kernel scope link src 10.244.2.1 ,交给cni0(这里会过宿主机iptables)
- cni0将包送给POD4
flannel容器启动的时候会给自己所在的node注入一些信息:
1 | #kubectl describe node hygon4 |grep -i flannel |
flannel.1 知道如何通过物理网卡打包网络包到目标地址,flanneld 会在每个host 添加 arp,以及将本机的 vxlan fdb 添加到新的 host上
1 | //这个 flannel 集群有四个 host,这是其中一个host |
包流程:
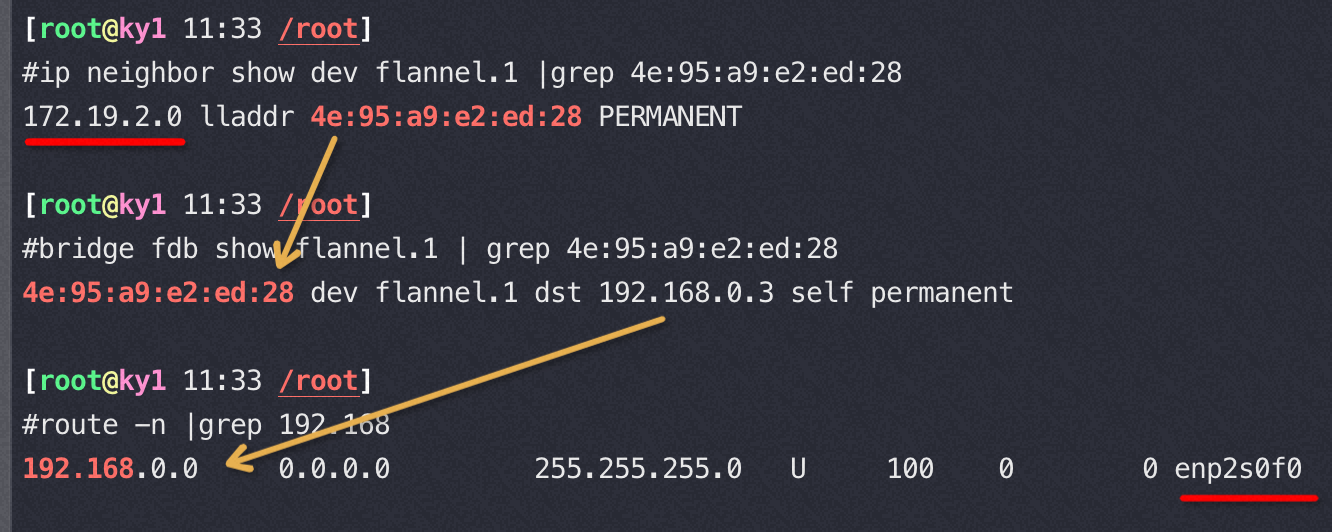
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table is used by a Layer 3 device (router, switch, server, desktop) to store the IP address to MAC address entries for a specific network device.
The FDB (forwarding database) table is used by a Layer 2 device (switch/bridge) to store the MAC addresses that have been learned and which ports that MAC address was learned on. The MAC addresses are learned through transparent bridging on switches and dedicated bridges.
抓包演示packet流转以及封包解包
一次完整的抓包过程演示包的流转,从hygon3上的pod 192.168.0.4(22:d8:63:6c:e8:96) 访问 hygon4上的pod 192.168.2.56(52:e6:8e:02:80:35)
1 | //hygon3上的pod 192.168.0.4(22:d8:63:6c:e8:96) 访问 hygon4上的pod 192.168.2.56(52:e6:8e:02:80:35),在cni0(a2:99:4f:dc:9d:5c)上抓包,跨机不走peer veth |
这个流转流程如下图:
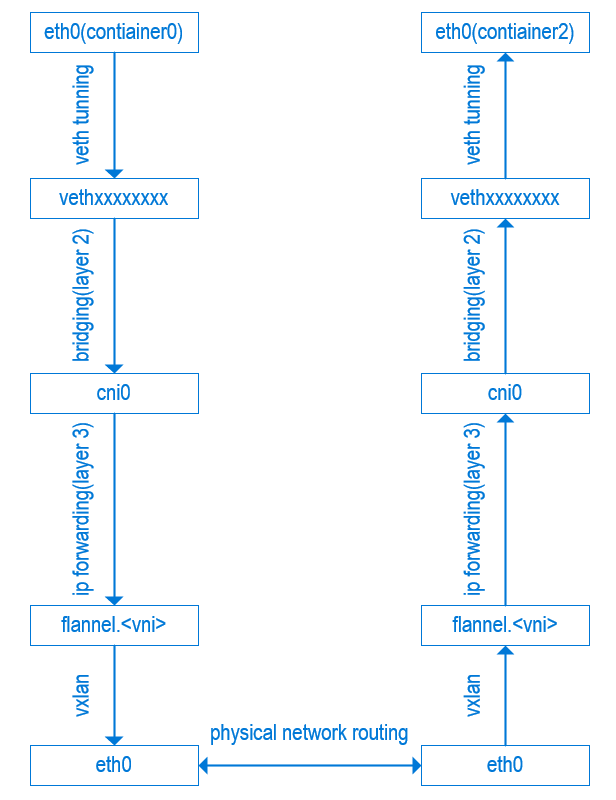
对应宿主机查询到的ip、路由信息(和上图不是对应的)
1 | #ip -d -4 addr show cni0 |
包流转示意图
flannel网络不通排查案例
当网络不通时,可以根据以上演示的包流转路径在不同的网络设备上抓包来定位哪个环节不通
firewalld
在麒麟系统的物理机上通过kubeadm setup集群,发现有的环境flannel网络不通,在宿主机上ping 其它物理机flannel.0网卡的ip,通过在对端宿主机抓包发现icmp收到后被防火墙扔掉了,抓包中可以看到错误信息:icmp unreachable - admin prohibited
下图中正常的icmp是直接ping 物理机ip
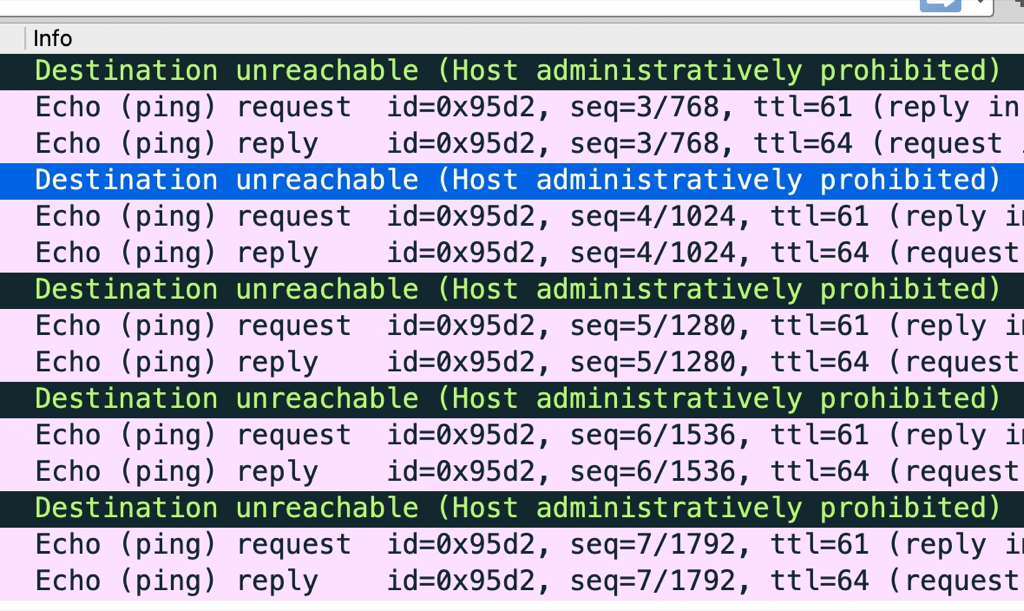
The “admin prohibited filter” seen in the tcpdump output means there is a firewall blocking a connection. It does it by sending back an ICMP packet meaning precisely that: the admin of that firewall doesn’t want those packets to get through. It could be a firewall at the destination site. It could be a firewall in between. It could be iptables on the Linux system.
发现有问题的环境中宿主机的防火墙设置报错了:
1 | 12月 28 23:35:08 hygon253 firewalld[10493]: WARNING: COMMAND_FAILED: '/usr/sbin/iptables -w10 -t filter -X DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1' failed: iptables: No chain/target/match by that name. |
应该是因为启动docker的时候 firewalld 是运行着的
Do you have firewalld enabled, and was it (re)started after docker was started? If so, then it’s likely that firewalld wiped docker’s IPTables rules. Restarting the docker daemon should re-create those rules.
停掉 firewalld 服务可以解决这个问题,k8s集群
flannel网络不通
Starting from Docker 1.13 default iptables policy for FORWARDING is DROP
flannel能收到包,但是cni0收不到包,说明包进到了目标宿主机,但是从flannel解开udp转送到cni的时候出了问题,大概率是iptables 拦截了包
1 | It seems docker version >=1.13 will add iptables rule like below,and it make this issue happen: |
宿主机多 ip 下 flannel 网络不通
宿主机有两个ip,flannel组网ip是192.168,但是默认路由在1.1.网络下,此时能 ping 通,但是curl不通端口
1 | #tcpdump -i enp2s0f0 -nettvv host 192.168.0.3 and udp |
多ip宿主机的网卡及路由
1 | 5: enp125s0f3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 |
解决办法:真正生效的是 flannel.1 中的地址
1 | //比如 flannel 选用了以下公网ip(默认路由上的ip)导致flannel网络不通,应该选内网ip |
解决办法得先删掉 flannel 网络,然后在 flannel.yaml 中指定内网网卡:
1 | containers: |
If you happen to have different interfaces to be matched, you can match it on a regex pattern. Let’s say the worker nodes could’ve enp0s8 or enp0s9 configured, then the flannel args would be
— --iface-regex=[enp0s8|enp0s9]
修改node的annotation中flannel的 public-ip。如果因为 public-ip 不对导致网络不通,在annotation中修改public-ip没用,这个值是 flannel 读取underlay 网络配置后写进来的,同时也写到了 flannel.1 的 config 中
1 | kubectl annotate node ky1 flannel.alpha.coreos.com/public-ip- |
容器调试
可以起一个容器,里面带有各种工具,然后attach 到目标容器 :https://github.com/zeromake/docker-debug/blob/master/README-zh-Hans.md
1 | ./docker-debug-linux-amd64 --image=CentOS8 nginx top -Hp 12 //可以先把工具安装在CentOS8,然后attach 到被调试的 nginx容器 |
抓包和调试 – nsenter
1 | 获取pid:docker inspect -f {{.State.Pid}} c8f874efea06 |
nsenter相当于在setns的示例程序之上做了一层封装,使我们无需指定命名空间的文件描述符,而是指定进程号即可,详细case
1 | #docker inspect cb7b05d82153 | grep -i SandboxKey //根据 pause 容器id找network namespace |
清理
cni信息
1 | /etc/cni/net.d/* |
calico创建的tunl0网卡是个tunnel,可以通过 ip tunnel show来查看,清理不掉(重启可以清理掉tunl0)
1 | ip link set dev tunl0 name tunl0_fallback |
清理和创建flannel网络
查看容器网卡和宿主机上的虚拟网卡veth pair:
1 | ip link //宿主机上执行 |
清理
1 | ip link delete cni0 |
创建
1 | ip link add cni0 type bridge |
完全可以手工创建cni0、flannel.1等网络设备,然后将 veth添加到cni0网桥上,再在宿主机配置ip route,基本一个纯手工版本打造的flannel vxlan网络就实现了,深入理解到此任何flannel网络问题都可以解决了。
flannel ip在多个node之间分配错乱
当铲掉重新部署的时候可能cni等网络有残留,导致下一次部署会报ip已存在的错误
1 | (combined from similar events): Failed create pod sandbox: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to set up sandbox container "f7aa44bf81b27bf0ff6c02339df2d2743cf952c1519fead4c563892d2d41a979" network for pod "nginx-deployment-6c8c86b759-f8fb7": NetworkPlugin cni failed to set up pod "nginx-deployment-6c8c86b759-f8fb7_default" network: failed to set bridge addr: "cni0" already has an IP address different from 172.19.2.1/24 |
可以铲掉网卡重新分配,或者给cni重新分配错误信息提示的ip
1 | ifconfig cni0 172.19.2.1/24 |
or
1 | ip link set cni0 down && ip link set flannel.1 down |
host-gw
实现超级简单,就是在宿主机上配置路由规则,把其它宿主机ip当成其上所有pod的下一跳,不用封包解包,所以性能奇好,但是要求所有宿主机在一个2层网络,因为ip路由规则要求是直达其它宿主机。
手工配置实现就是vxlan的超级精简版,略!
netns 操作
以下case创建一个名为 ren 的netns,然后在里面增加一对虚拟网卡veth1 veth1_p, veth1放置在ren里面,veth1_p 放在物理机上,给他们配置上ip并up就能通了。
1 | 1004 [2021-10-27 10:49:08] ip netns add ren |
Linux 上存在一个默认的网络命名空间,Linux 中的 1 号进程初始使用该默认空间。Linux 上其它所有进程都是由 1 号进程派生出来的,在派生 clone 的时候如果没有额外特别指定,所有的进程都将共享这个默认网络空间。
所有的网络设备刚创建出来都是在宿主机默认网络空间下的。可以通过 ip link set 设备名 netns 网络空间名 将设备移动到另外一个空间里去,socket也是归属在某一个网络命名空间下的,由创建socket进程所在的netns来决定socket所在的netns
1 | //file: net/socket.c |
内核提供了三种操作命名空间的方式,分别是 clone、setns 和 unshare。ip netns add 使用的是 unshare,原理和 clone 是类似的。
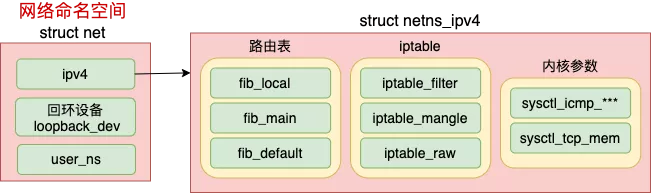
每个 net 下都包含了自己的路由表、iptable 以及内核参数配置等等
etcd 中存储的 flannel 配置
1 | kubectl exec -it etcd-uos21 -n=kube-system -- /bin/sh |
总结
通过无论是对flannel还是calico的学习,不管是使用vxlan还是host-gw发现这些所谓的overlay网络不过是披着一层udp的皮而已,只要我们对ip route/mac地址足够了解,这些新技术剖析下来仍然逃不过 RFC1180 描述的几个最基础的知识点(基础知识的力量)的使用而已,这一切硬核的基础知识无比简单,只要你多看看我这篇旧文《就是要你懂网络–一个网络包的旅程》
参考资料
https://morven.life/notes/networking-3-ipip/
https://www.cnblogs.com/bakari/p/10564347.html