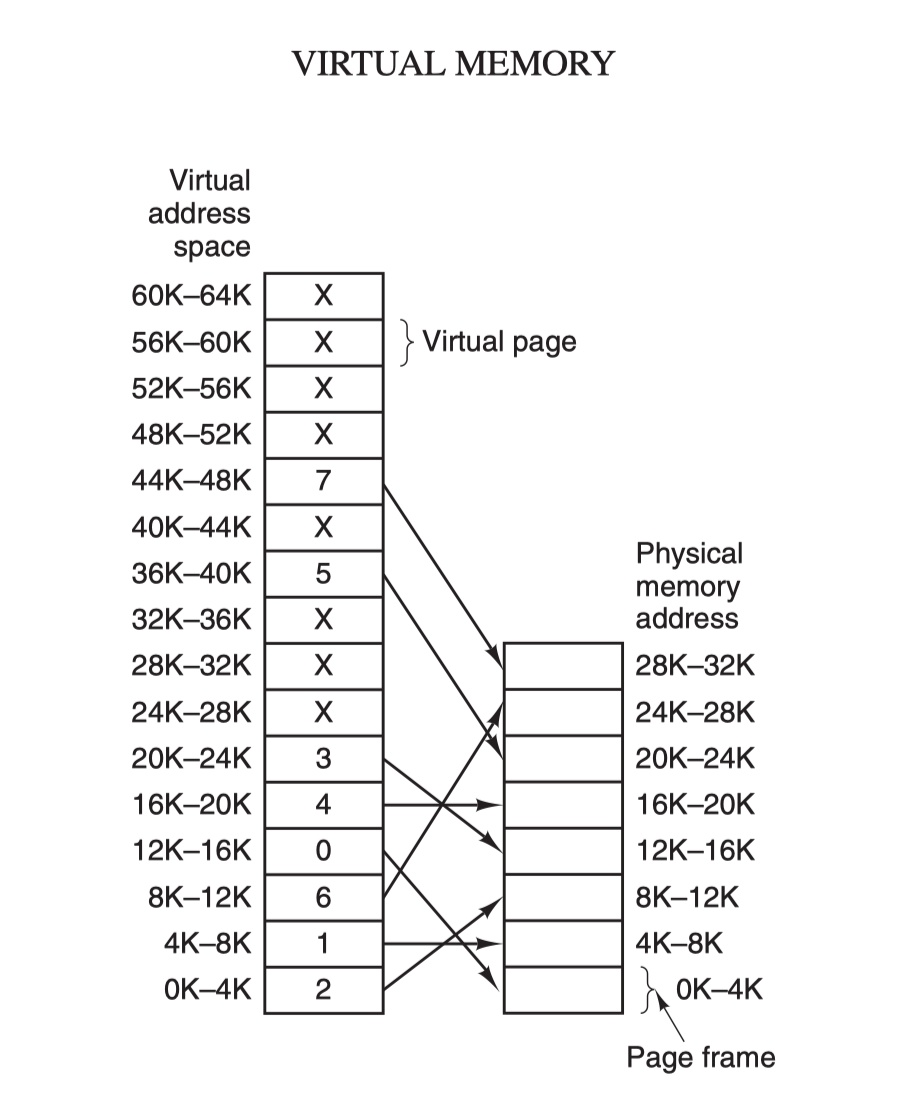
到底一台服务器上最多能创建多少个TCP连接
到底一台服务器上最多能创建多少个TCP连接
经常听到有同学说一台机器最多能创建65535个TCP连接,这其实是错误的理解,为什么会有这个错误的理解呢?
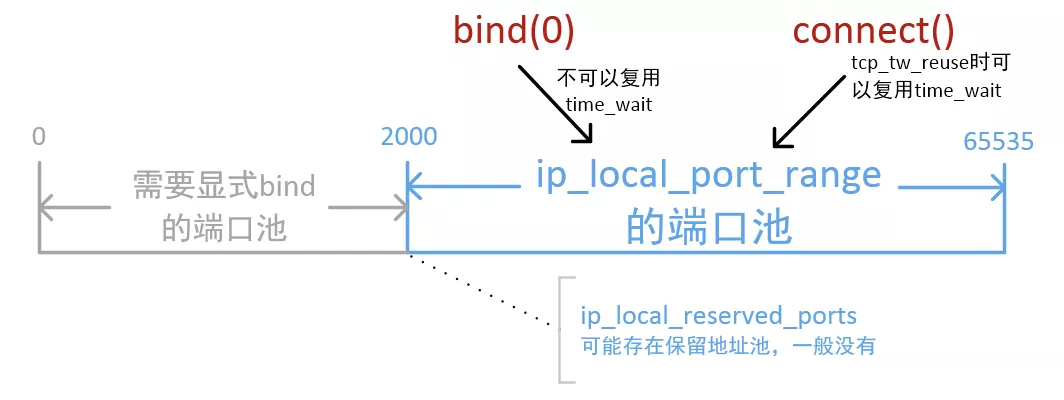
port range
我们都知道linux下本地随机端口范围由参数控制,也就是listen、connect时候如果没有指定本地端口,那么就从下面的port range 中随机取一个可用的
1 | # cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range |
port range的上限是65535,所以也经常看到这个误解:一台机器上最多能创建65535个TCP连接
到底一台机器上最多能创建多少个TCP连接
先说结论:在内存、文件句柄足够的话可以创建的连接是没有限制的(每个TCP连接至少要消耗一个文件句柄)。
那么/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range指定的端口范围到底是什么意思呢?
核心规则:一个TCP连接只要保证四元组(src-ip src-port dest-ip dest-port)唯一就可以了,而不是要求src port唯一
后面所讲都遵循这个规则,所以在心里反复默念:四元组唯一 五个大字,就能分析出来到底能创建多少TCP连接了。
比如如下这个机器上的TCP连接实际状态:
1 | # netstat -ant |grep 18089 |
从前三行可以清楚地看到18089被用了三次,第一第二行src-ip、dest-ip也是重复的,但是dest port不一样,第三行的src-port还是18089,但是src-ip变了。他们的四元组均不相同。
所以一台机器能创建的TCP连接是没有限制的,而ip_local_port_range是指没有bind的时候OS随机分配端口的范围,但是分配到的端口要同时满足五元组唯一,这样 ip_local_port_range 限制的是连同一个目标(dest-ip和dest-port一样)的port的数量(请忽略本地多网卡的情况,因为dest-ip为以后route只会选用一个本地ip)。
**那么为什么大家有这样的误解呢?**我总结了下,大概是以下两个原因让大家误解了:
- 如果是listen服务,那么肯定端口不能重复使用,这样就跟我们的误解对应上了,一个服务器上最多能监听65535个端口。比如nginx监听了80端口,那么tomcat就没法再监听80端口了,这里的80端口只能监听一次。
- 另外如果我们要连的server只有一个,比如:1.1.1.1:80 ,同时本机只有一个ip的话,那么这个时候即使直接调connect 也只能创建出65535个连接,因为四元组中的三个是固定的了。
我们在创建连接前,经常会先调bind,bind后可以调 listen当做服务端监听,也可以直接调connect当做client来连服务端。
bind(ip,port=0) 的时候是让系统绑定到某个网卡和自动分配的端口,此时系统没有办法确定接这个socket 是要去connect还是listen. 如果是listen的话,那么肯定是不能出现端口冲突的(得local port 唯一),如果是connect的话,只要满足4元组唯一即可。在这种情况下,系统只能尽可能满足更强的要求,就是先要求端口不能冲突,即使之后去connect的时候四元组是唯一的。
比如 Nginx HaProxy envoy这些软件在创建到upstream的连接时,都会用 bind(0) 的方式, 导致到不同目的的连接无法复用同一个src port,这样后端的最大连接数受限于local_port_range。 nginx的修改 http://hg.nginx.org/nginx/rev/2c7b488a61fb
Linux 4.2后的内核增加了IP_BIND_ADDRESS_NO_PORT 这个socket option来解决这个问题,将src port的选择延后到connect的时候
IP_BIND_ADDRESS_NO_PORT (since Linux 4.2)
Inform the kernel to not reserve an ephemeral port when using bind(2) with a port number of 0. The port will later be automatically chosen at connect(2) time, in a way that allows sharing a source port as long as the 4-tuple is unique.
但如果我只是个client端,只需要连接server建立连接,也就不需要bind,直接调connect就可以了,这个时候只要保证四元组唯一就行。
bind()的时候内核是还不知道四元组的,只知道src_ip、src_port,所以这个时候单网卡下src_port是没法重复的,但是connect()的时候已经知道了四元组的全部信息,所以只要保证四元组唯一就可以了,那么这里的src_port完全是可以重复使用的。
是不是加上了 SO_REUSEADDR、SO_REUSEPORT 就能重用端口了呢?
TCP SO_REUSEADDR
文档描述:
SO_REUSEADDR Indicates that the rules used in validating addresses supplied in a bind(2) call should allow reuse of local addresses. For AF_INET sockets this means that a socket may bind, except when there is an active listening socket bound to the address. When the listening socket is bound to INADDR_ANY with a specific port then it is not possible to bind to this port for any local address. Argument is an integer boolean flag.
从这段文档中我们可以知道三个事:
- 使用这个参数后,bind操作是可以重复使用local address的,注意,这里说的是local address,即ip加端口组成的本地地址,如果机器有两个本地ip,那么任意ip或端口部分不一样,它们本身就是可以共存的,不需要使用这个参数。
- 当local address被一个处于listen状态的socket使用时,加上该参数也不能重用这个地址。
- 当处于listen状态的socket监听的本地地址的ip部分是INADDR_ANY,即表示监听本地的所有ip,即使使用这个参数,也不能再bind包含这个端口的任意本地地址,这个和 2 中描述的其实是一样的。
==SO_REUSEADDR 可以用本地相同的(sip, sport) 去连connect 远程的不同的(dip、dport)//而 SO_REUSEPORT主要是解决Server端的port重用==
SO_REUSEADDR 还可以重用TIME_WAIT状态的port, 在程序崩溃后之前的TCP连接会进入到TIME_WAIT状态,需要一段时间才能释放,如果立即重启就会抛出Address Already in use的错误导致启动失败。这时候可以通过在调用bind函数之前设置SO_REUSEADDR来解决。
What exactly does SO_REUSEADDR do?
This socket option tells the kernel that even if this port is busy (in the TIME_WAIT state), go ahead and reuse it anyway. If it is busy, but with another state, you will still get an address already in use error. It is useful if your server has been shut down, and then restarted right away while sockets are still active on its port. You should be aware that if any unexpected data comes in, it may confuse your server, but while this is possible, it is not likely.
It has been pointed out that “A socket is a 5 tuple (proto, local addr, local port, remote addr, remote port). SO_REUSEADDR just says that you can reuse local addresses. The 5 tuple still must be unique!” This is true, and this is why it is very unlikely that unexpected data will ever be seen by your server. The danger is that such a 5 tuple is still floating around on the net, and while it is bouncing around, a new connection from the same client, on the same system, happens to get the same remote port.
By setting SO_REUSEADDR user informs the kernel of an intention to share the bound port with anyone else, but only if it doesn’t cause a conflict on the protocol layer. There are at least three situations when this flag is useful:
- Normally after binding to a port and stopping a server it’s neccesary to wait for a socket to time out before another server can bind to the same port. With
SO_REUSEADDRset it’s possible to rebind immediately, even if the socket is in aTIME_WAITstate. - When one server binds to
INADDR_ANY, say0.0.0.0:1234, it’s impossible to have another server binding to a specific address like192.168.1.21:1234. WithSO_REUSEADDRflag this behaviour is allowed. - When using the bind before connect trick only a single connection can use a single outgoing source port. With this flag, it’s possible for many connections to reuse the same source port, given that they connect to different destination addresses.
TCP SO_REUSEPORT
SO_REUSEPORT主要用来解决惊群、性能等问题。通过多个进程、线程来监听同一端口,进来的连接通过内核来hash分发做到负载均衡,避免惊群。
SO_REUSEPORT is also useful for eliminating the try-10-times-to-bind hack in ftpd’s data connection setup routine. Without SO_REUSEPORT, only one ftpd thread can bind to TCP (lhost, lport, INADDR_ANY, 0) in preparation for connecting back to the client. Under conditions of heavy load, there are more threads colliding here than the try-10-times hack can accomodate. With SO_REUSEPORT, things work nicely and the hack becomes unnecessary.
SO_REUSEPORT使用场景:linux kernel 3.9 引入了最新的SO_REUSEPORT选项,使得多进程或者多线程创建多个绑定同一个ip:port的监听socket,提高服务器的接收链接的并发能力,程序的扩展性更好;此时需要设置SO_REUSEPORT(注意所有进程都要设置才生效)。
setsockopt(listenfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT,(const void *)&reuse , sizeof(int));
目的:每一个进程有一个独立的监听socket,并且bind相同的ip:port,独立的listen()和accept();提高接收连接的能力。(例如nginx多进程同时监听同一个ip:port)
(a) on Linux SO_REUSEPORT is meant to be used purely for load balancing multiple incoming UDP packets or incoming TCP connection requests across multiple sockets belonging to the same app. ie. it’s a work around for machines with a lot of cpus, handling heavy load, where a single listening socket becomes a bottleneck because of cross-thread contention on the in-kernel socket lock (and state).
(b) set IP_BIND_ADDRESS_NO_PORT socket option for tcp sockets before binding to a specific source ip
with port 0 if you’re going to use the socket for connect() rather then listen() this allows the kernel
to delay allocating the source port until connect() time at which point it is much cheaper
The Ephemeral Port Range
Ephemeral Port Range就是我们前面所说的Port Range(/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range)
A TCP/IPv4 connection consists of two endpoints, and each endpoint consists of an IP address and a port number. Therefore, when a client user connects to a server computer, an established connection can be thought of as the 4-tuple of (server IP, server port, client IP, client port).
Usually three of the four are readily known – client machine uses its own IP address and when connecting to a remote service, the server machine’s IP address and service port number are required.
What is not immediately evident is that when a connection is established that the client side of the connection uses a port number. Unless a client program explicitly requests a specific port number, the port number used is an ephemeral port number.
Ephemeral ports are temporary ports assigned by a machine’s IP stack, and are assigned from a designated range of ports for this purpose. When the connection terminates, the ephemeral port is available for reuse, although most IP stacks won’t reuse that port number until the entire pool of ephemeral ports have been used.
So, if the client program reconnects, it will be assigned a different ephemeral port number for its side of the new connection.
linux 如何选择Ephemeral Port
有资料说是随机从Port Range选择port,有的说是顺序选择,那么实际验证一下。
如下测试代码:
1 | #include <stdio.h> // printf |
bind逻辑测试代码
1 | #include <netinet/in.h> |
3.10.0-327.ali2017.alios7.x86_64
编译后,执行(3.10.0-327.ali2017.alios7.x86_64):
1 | #date; ./client && echo "+++++++" ; ./client && sleep 0.1 ; echo "-------" && ./client && sleep 10; date; ./client && echo "+++++++" ; ./client && sleep 0.1 && echo "******"; ./client; |
从测试看起来linux下端口选择跟时间有关系,起始端口肯定是顺序增加,起始端口应该是在Ephemeral Port范围内并且和时间戳绑定的某个值(也是递增的),即使没有使用任何端口,起始端口也会随时间增加而增加。
4.19.91-19.1.al7.x86_64
换个内核版本编译后,执行(4.19.91-19.1.al7.x86_64):
1 | $date; ./client && echo "+++++++" ; ./client && sleep 0.1 ; echo "-------" && ./client && sleep 10; date; ./client && echo "+++++++" ; ./client && sleep 0.1 && echo "******"; ./client; |
以上测试时的参数
1 | $cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range |
将1024改成1025后,分配出来的都是奇数端口了:
1 | $cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range |
之所以都是偶数端口,是因为port_range 从偶数开始, 每次从++变到+2的原因,connect挑选随机端口时都是在起始端口的基础上+2,而bind挑选随机端口的起始端口是系统port_range起始端口+1(这样和connect错开),然后每次仍然尝试+2,这样connect和bind基本一个用偶数另外一个就用奇数,一旦不够了再尝试使用另外一组
1 | $cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range |
可见4.19内核下每次port是+2,在3.10内核版本中是+1. 并且都是递增的,同时即使port不使用,也会随着时间的变化这个起始port增大。
Port Range有点像雷达转盘数字,时间就像是雷达上的扫描指针,这个指针不停地旋转,如果这个时候刚好有应用要申请Port,那么就从指针正好指向的Port开始向后搜索可用port
tcp_max_tw_buckets
tcp_max_tw_buckets: 在 TIME_WAIT 数量等于 tcp_max_tw_buckets 时,新的连接断开不再进入TIME_WAIT阶段,而是直接断开,并打印warnning.
实际测试发现 在 TIME_WAIT 数量等于 tcp_max_tw_buckets 时 新的连接仍然可以不断地创建和断开,这个参数大小不会影响性能,只是影响TIME_WAIT 数量的展示(当然 TIME_WAIT 太多导致local port不够除外), 这个值设置小一点会避免出现端口不够的情况
tcp_max_tw_buckets - INTEGER
Maximal number of timewait sockets held by system simultaneously.If this number is exceeded time-wait socket is immediately destroyed and warning is printed. This limit exists only to prevent simple DoS attacks, you must not lower the limit artificially, but rather increase it (probably, after increasing installed memory), if network conditions require more than default value.
监控指标:
1 | netstat -s | grep TCPTimeWaitOverflow |
SO_LINGER
SO_LINGER选项用来设置延迟关闭的时间,等待套接字发送缓冲区中的数据发送完成。 没有设置该选项时,在调用close() 后,在发送完FIN后会立即进行一些清理工作并返回。 如果设置了SO_LINGER选项,并且等待时间为正值,则在清理之前会等待一段时间。
如果把延时设置为 0 时,Socket就丢弃数据,并向对方发送一个 RST 来终止连接,因为走的是 RST 包,所以就不会有 TIME_WAIT 了。
This option specifies how the
closefunction operates for a connection-oriented protocol (for TCP, but not for UDP). By default,closereturns immediately, but ==if there is any data still remaining in the socket send buffer, the system will try to deliver the data to the peer==.
SO_LINGER 有三种情况
- l_onoff 为false(0), 那么 l_linger 的值没有意义,socket主动调用close时会立即返回,操作系统会将残留在缓冲区中的数据发送到对端,并按照正常流程关闭(交换FIN-ACK),最后连接进入
TIME_WAIT状态。这是默认情况 - l_onoff 为true(非0), l_linger 为0,主动调用close的一方也是立刻返回,但是这时TCP会丢弃发送缓冲中的数据,而且不是按照正常流程关闭连接(不发送FIN包),直接发送
RST,连接不会进入 time_wait 状态,对端会收到java.net.SocketException: Connection reset异常 - l_onoff 为true(非0), l_linger 也为非 0,这表示
SO_LINGER选项生效,并且超时时间大于零,这时调用close的线程被阻塞,TCP会发送缓冲区中的残留数据,这时有两种可能的情况:- 数据发送完毕,收到对方的ACK,然后进行连接的正常关闭(交换FIN-ACK)
- 超时,未发送完(指没收到对端的 ACK)的数据被丢弃,发送
RST进行非正常关闭
1 | struct linger { |
NIO下设置 SO_LINGER 的错误案例
在使用NIO时,最好不设置SO_LINGER。比如Tomcat服务端接收到请求创建新连接时,做了这样的设置:
1 | SocketChannel.setOption(SocketOption.SO_LINGER, 1000) |
SO_LINGER的单位为秒!在网络环境比较好的时候,例如客户端、服务器都部署在同一个机房,close虽然会被阻塞,但时间极短可以忽略。但当网络环境不那么好时,例如存在丢包、较长的网络延迟,buffer中的数据一直无法发送成功,那么问题就出现了:close会被阻塞较长的时间,从而直接或间接引起NIO的IO线程被阻塞,服务器会不响应,不能处理accept、read、write等任何IO事件。也就是应用频繁出现挂起现象。解决方法就是删掉这个设置,close时立即返回,由操作系统接手后面的工作。
被阻塞时会看到如下连接状态:
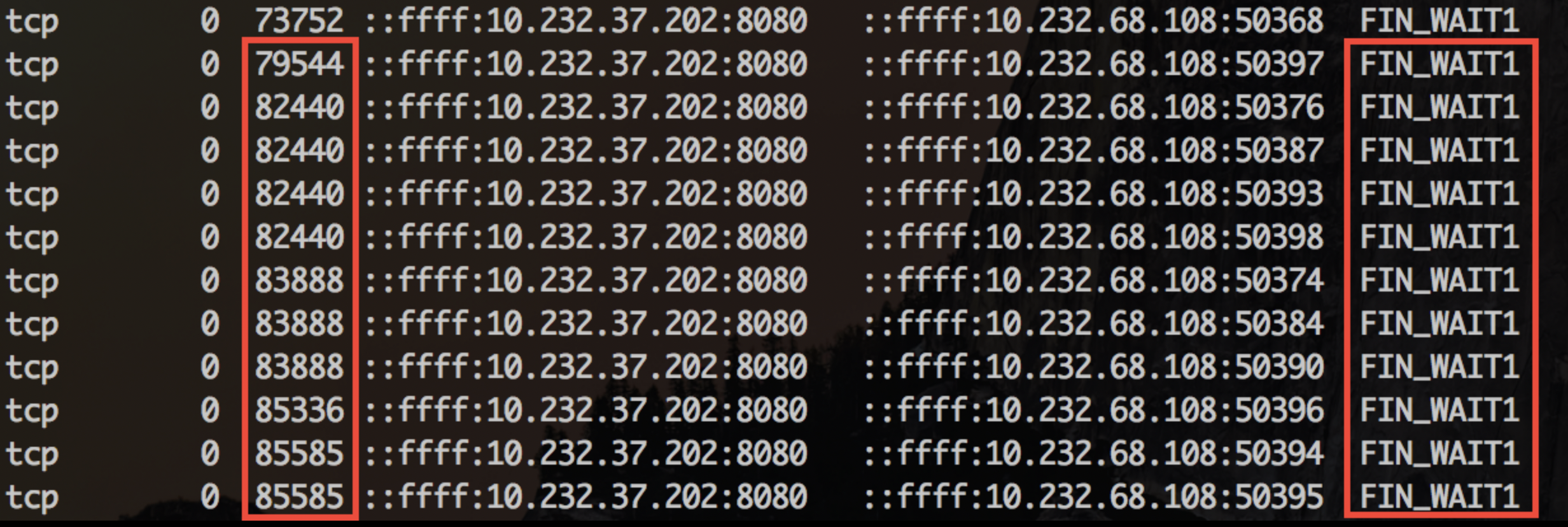
以及对应的堆栈
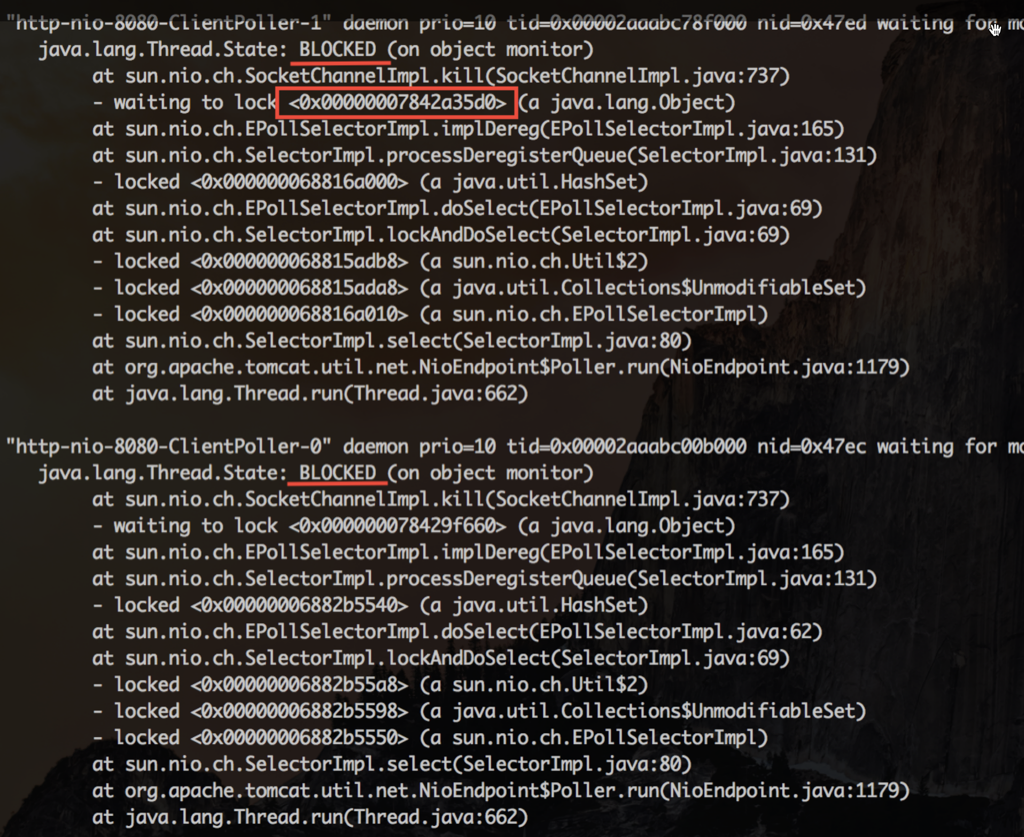
查看其中一个IO线程等待的锁,发现锁是被HTTP线程持有。这个线程正在执行preClose0,就是在这里等待连接的关闭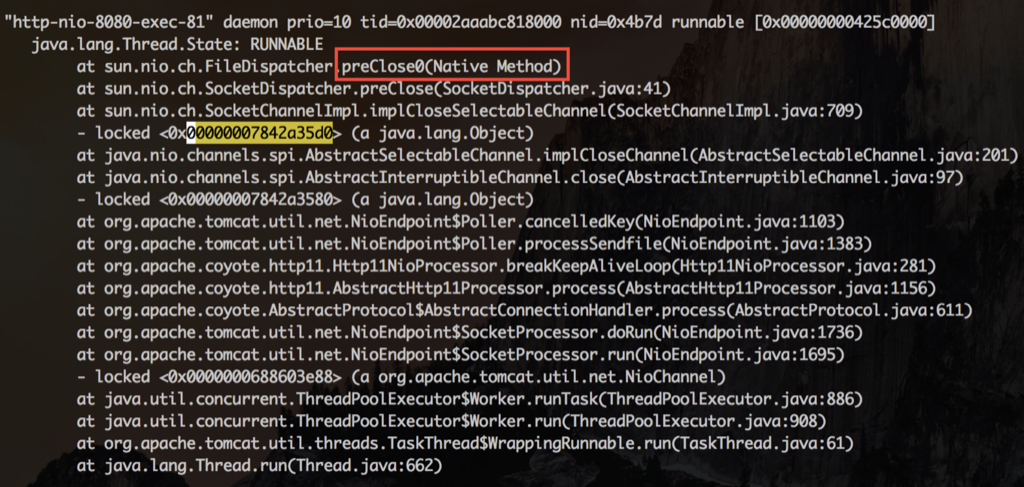
每次HTTP线程在关闭连接被阻塞时,同时持有了SocketChannelImpl的对象锁,而 IO线程在把这个连接移除出它的 selector管理队列时,也要获得同一个SocketChannelImpl的对象锁。IO 线程就这么一次次的被阻塞,悲剧的无以复加。有些 NIO框架会让 IO线程去做close,这时候就更加悲剧了。
总之这里的错误原因有两点:1)网络状态不好;2)错误理解了l_linger 的单位,是秒,不是毫秒。 在这两个原因的共同作用下导致了数据迟迟不能发送完毕,l_linger 超时又需要很久,所以服务会出现一直阻塞的状态。
为什么要有 time_wait 状态
TIME-WAIT - represents waiting for enough time to pass to be sure the remote TCP received the acknowledgment of its connection termination request.
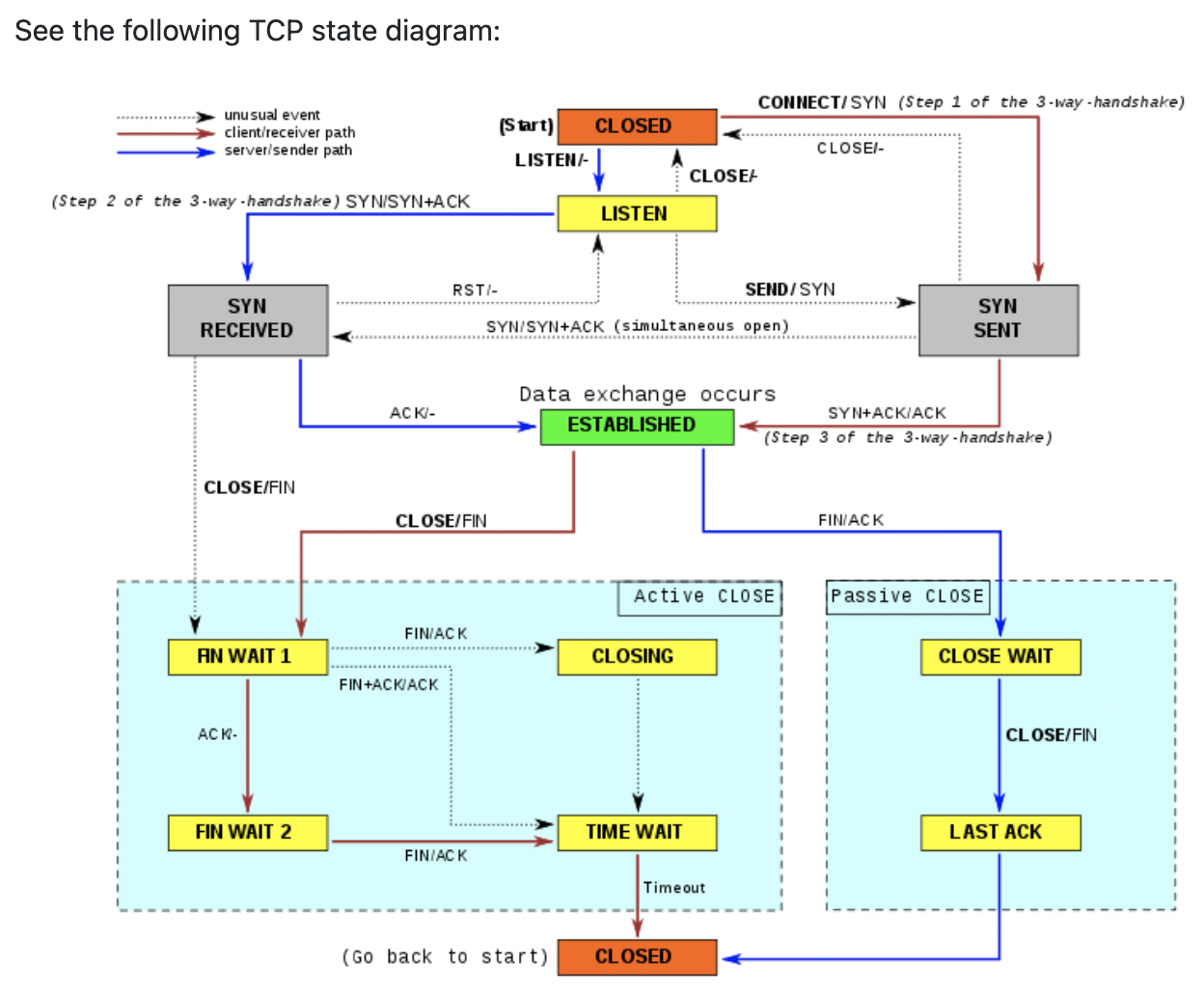
由Nginx SY CPU高负载引发内核探索之旅
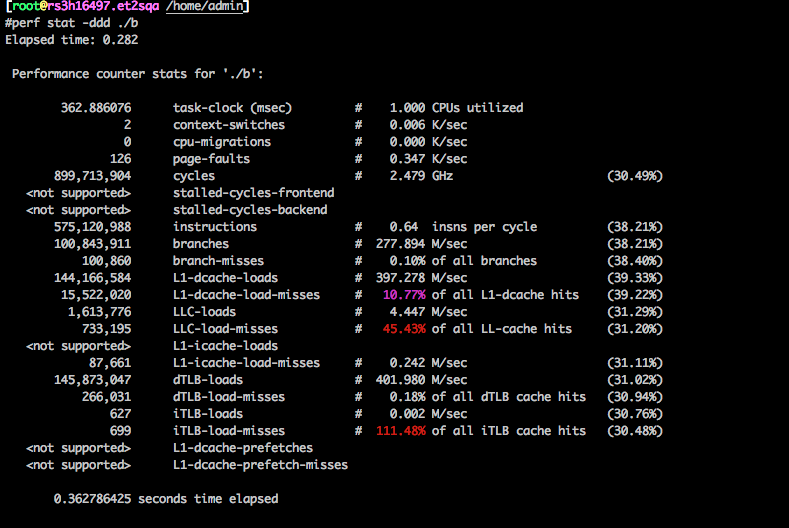
这个案例来自腾讯7层网关团队,网关用的Nginx,请求转发给后面的被代理机器(RS:real server),发现 sys CPU异常高,CPU都用在搜索可用端口.
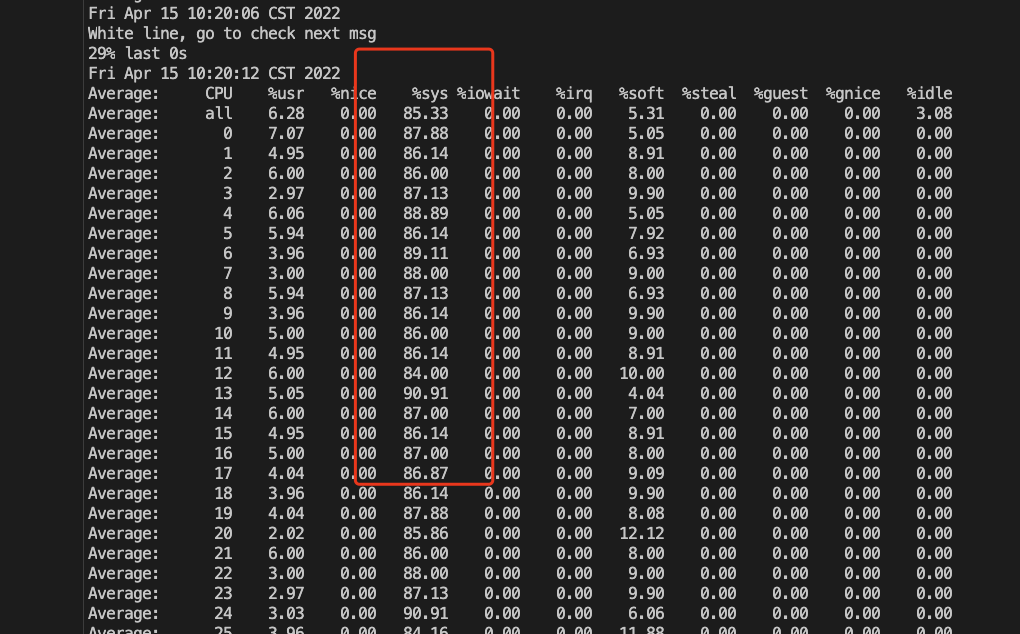
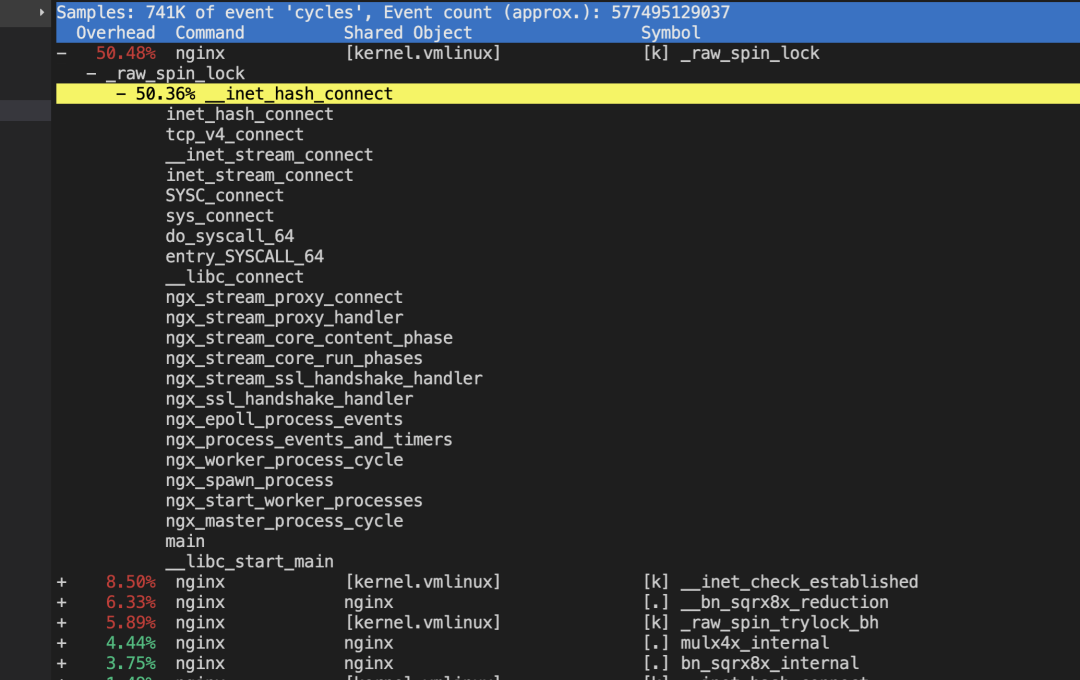

local port 不够的时候inet_hash_connect 中的spin_lock 会消耗过高的 sys(特别注意4.6内核后 local port 分奇偶数,每次loop+2,所以更容易触发port不够的场景)
核心原因总结: 4.6后内核把本地端口分成奇偶数,奇数给connect, 偶数给listen,本来端口有6万,这样connect只剩下3万,当这3万用完后也不会报找不到本地可用端口的错误(这里报错可能更好),而是在奇数里找不到就找偶数里的,每次都这样。 没改以前,总共6万端口,用掉3万,不分奇偶的话那么每找两个端口就有一个能用,也就是50%的概率。但是改了新的实现方案后,每次先要找奇数的3万个,全部在用,然后到偶数里继续找到第30001个才是可用的,也就是找到的概率变成了3万分之一,一下子复杂度高了15000倍,不慢才怪
对这个把端口分成奇偶数我的看法:这个做法就是坑爹货,在内核里胡乱搞,为了一个小场景搞崩大多数正常场景,真没必要,当然我这是事后诸葛亮,如果当时这种feature拿给我看我也会认为很不错,想不到这个坑点!
从STGW流量下降探秘内核收包机制
listen port search消耗CPU异常高
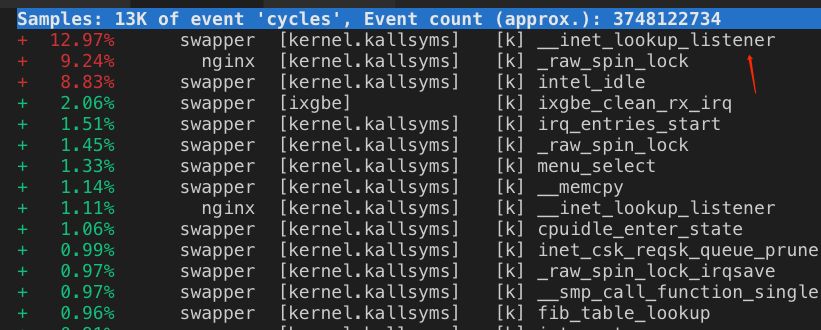
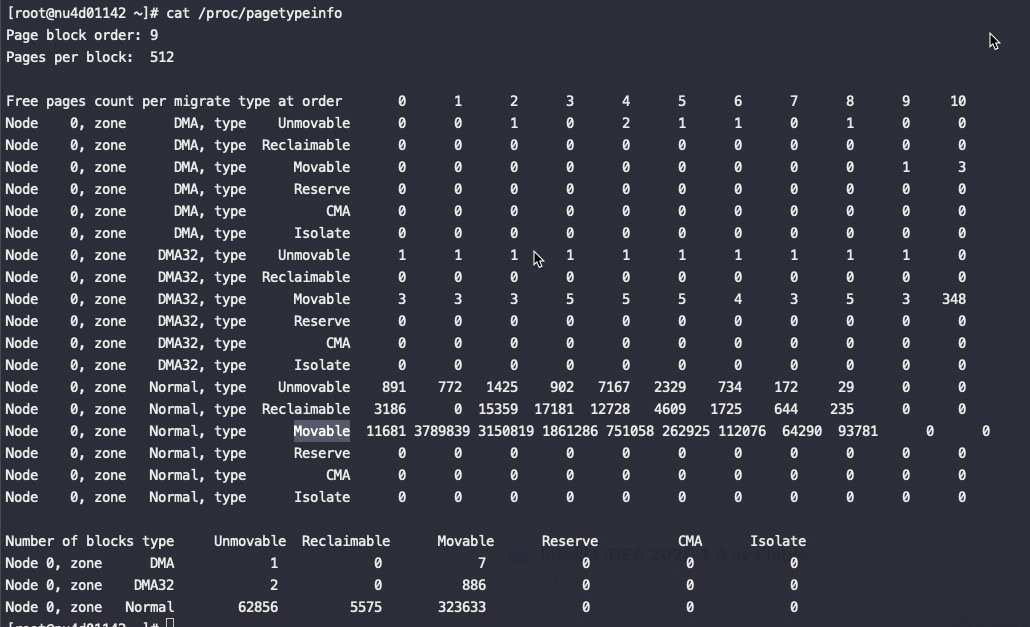
在正常的情况下,服务器的listen port数量,大概就是几w个这样的量级。这种量级下,一个port对应一个socket,哈希桶大小为32是可以接受的。
然而在内核支持了reuseport并且被广泛使用后,情况就不一样了,**在多进程架构里,listen port对应的socket数量,是会被几十倍的放大的。*以应用层监听了5000个端口,reuseport 使用了50个cpu核心为例,500050/32约等于7812,意味着每次握手包到来时,光是查找listen socket,就需要遍历7800多次。随着机器硬件性能越来越强,应用层使用的cpu数量增多,这个问题还会继续加剧。
正因为上述原因,并且我们现网机器开启了reuseport,在端口数量较多的机器里,inet_lookup_listener的哈希桶大小太小,遍历过程消耗了cpu,导致出现了函数热点。
短连接的开销
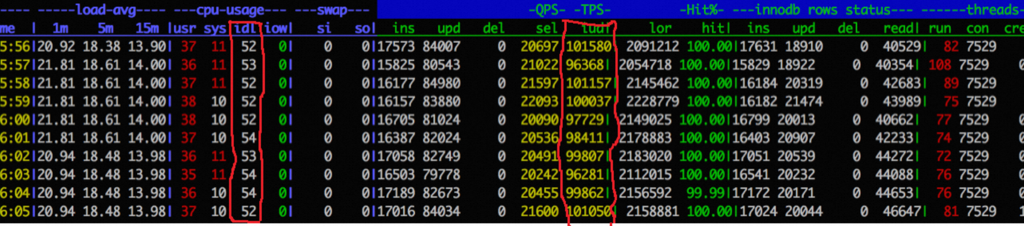
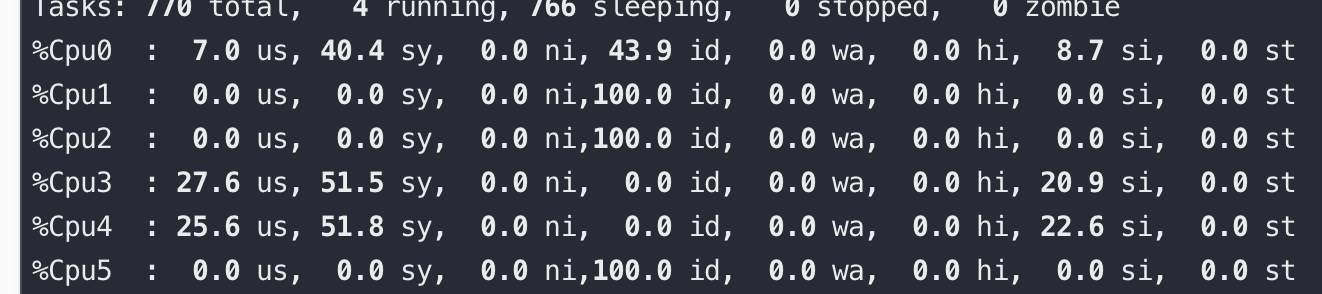
用ab通过短连接走 lo 网卡压本机 nginx,CPU0是 ab 进程,CPU3/4 是 Nginx 服务,可以看到 si 非常高,QPS 2.2万
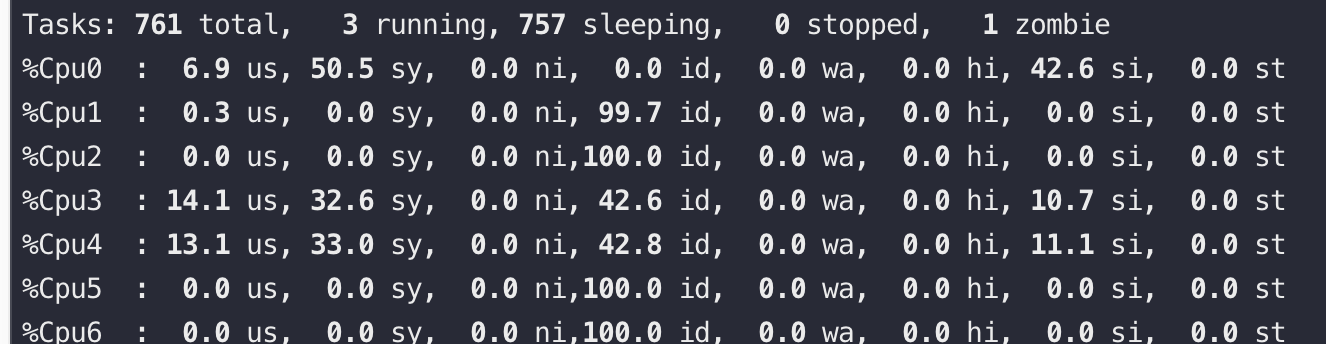
再将 ab 改用长连接来压,可以看到si、sy都有下降,并且 si 下降到短连接的20%,QPS 还能提升到 5.2万
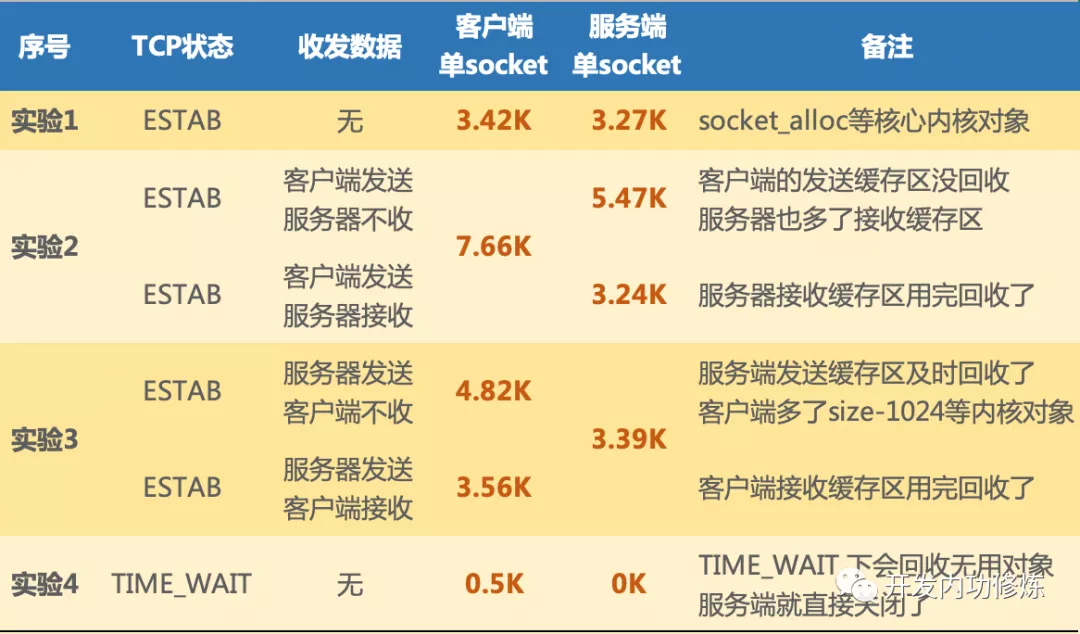
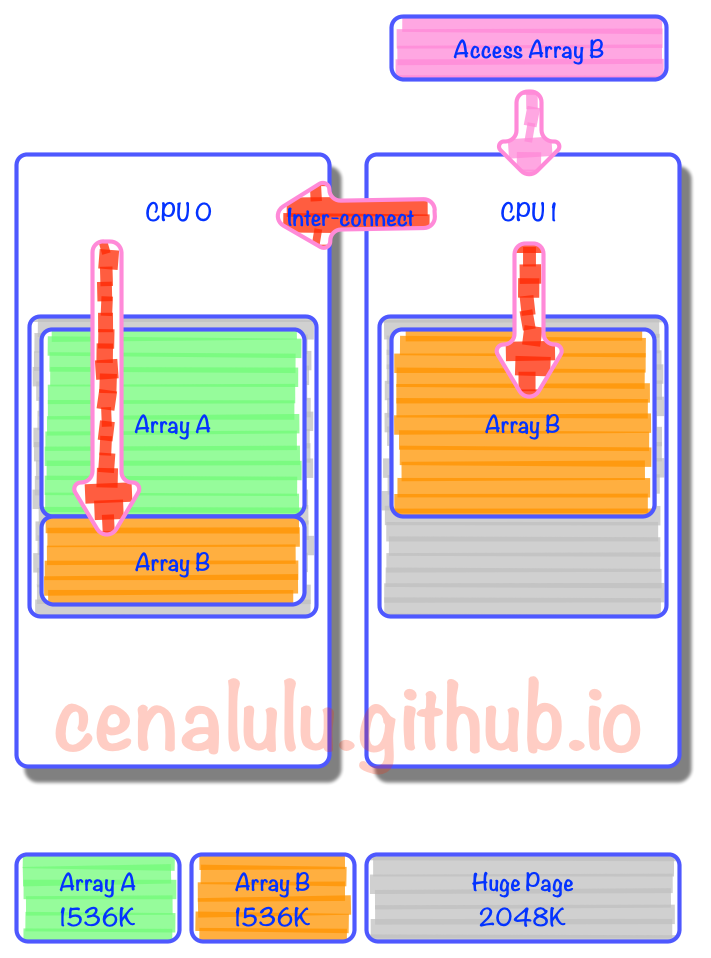
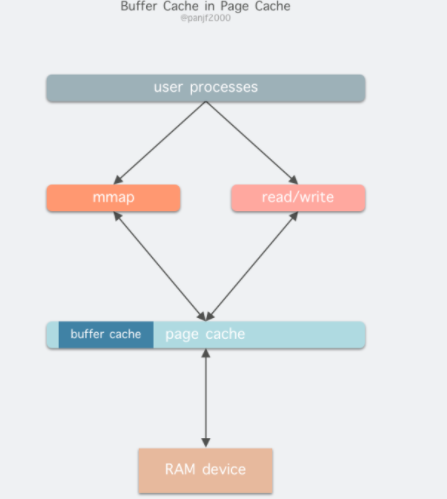
一条连接的开销
主要是内存开销(如图,来源见水印),另外就是每个连接都会占用一个文件句柄,可以通过参数来设置:fs.nr_open、nofile(其实 nofile 还分 soft 和 hard) 和 fs.file-max
从上图可以看到:
没有收发数据的时候收发buffer不用提前分配,3K多点的内存是指一个连接的元信息数据空间,不包含传输数据的内存buffer
客户端发送数据后,会根据数据大小分配send buffer(一般不超过wmem,默认kernel会根据系统内存压力来调整send buffer大小)
server端kernel收到数据后存放在rmem中,应用读走后就会释放对应的rmem
rmem和wmem都不会重用,用时分配用完释放
可见,内核在 socket 内存开销优化上采取了不少方法:
- 内核会尽量及时回收发送缓存区、接收缓存区,但高版本做的更好
- 发送接收缓存区最小并一定不是 rmem 内核参数里的最小值,实际大部分时间都是0
- 其它状态下,例如对于TIME_WAIT还会回收非必要的 socket_alloc 等对象
或者看这篇分析:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25241630
不同进程使用相同端口,设置SO_REUSEADDR后被bind 导致可用 local port 不够
A进程选择某个端口当local port 来connect,并设置了 reuseaddr opt(表示其它进程还能继续用这个端口),这时B进程选了这个端口,并且bind了,B进程用完后把这个bind的端口释放了,但是如果 A 进程一直不释放这个端口对应的连接,那么这个端口会一直在内核中记录被bind用掉了(能bind的端口 是65535个,四元组不重复的连接你理解可以无限多),这样的端口越来越多后,剩下可供 A 进程发起连接的本地随机端口就越来越少了(也就是本来A进程选择端口是按四元组的,但因为前面所说的原因,导致不按四元组了,只按端口本身这个一元组来排重),这时会造成新建连接的时候这个四元组高概率重复,一般这个时候对端大概率还在 time_wait 状态,会忽略掉握手 syn 包并回复 ack ,进而造成建连接卡顿的现象;超频繁的端口复用在LVS 场景下会产生问题,导致建连异常;或者syn包被 RST 触发1秒钟重传 syn
这个A、B进程共同跑在一台宿主机上很多年了,只因为之前是3.10内核,这次升级到了4.19后因为奇偶数放大了问题
当A进程已经开启了 SO_REUSEADDR 对外建联,此时 B 进程同样开启 SO_REUSEADDR 可以bind 此端口成功,当前端口就被设置为bind 状态,其他非 SO_REUSEADDR 的建联无法选到此端口
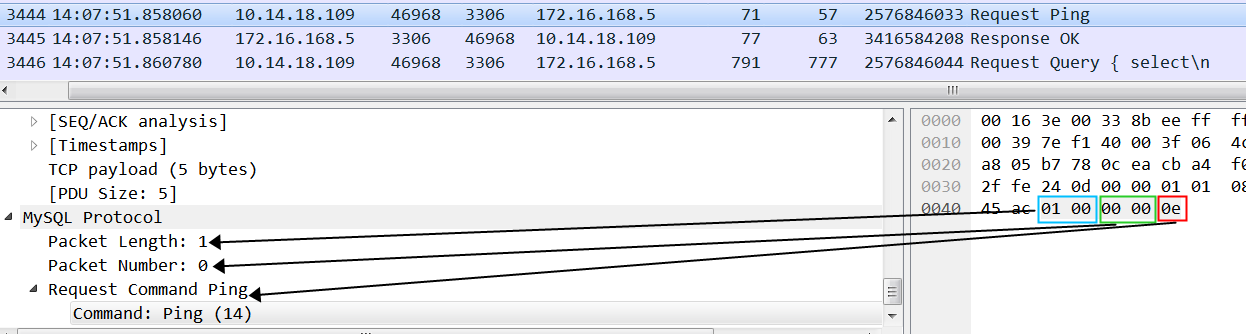
验证端口被connect 和 listen 同时使用
尝试先用 connect 把18181 端口用掉,然后在18181端口上起一个listen 服务,再从其他地方连这个listen的 18181端口

抓包,本机 ip 是 172.17.151.5 :

抓包里的 stream 1 对应上图的connect to baidu.com:80
抓包里的 stream 2 对应其它客户端连listen 18181上的服务,对应的netstat 信息:
1 | #netstat -anpo |grep 18181 |
可以得出如下结论:
两个TCP 连接四元组不一样,互相不干涉
先connect(SO_REUSEADDR) 用掉A端口后,还可以在上面继续使用A 端口来 listen(nc -l 18181)
先 listen 再connect 是不行的,报:Cannot assign requested address
结论
- 在内存、文件句柄足够的话一台服务器上可以创建的TCP连接数量是没有限制的
- SO_REUSEADDR 主要用于快速重用 TIME_WAIT状态的TCP端口,避免服务重启就会抛出Address Already in use的错误
- 先起一个listen 的端口设置了 SO_REUSEADDR,在其它进程 connect 的时候也不会从 port range 里再被选出来重用
- SO_REUSEPORT主要用来解决惊群、性能等问题
- 全局范围可以用 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 50000 来限制总 time_wait 数量,但是会掩盖问题
- local port的选择是递增搜索的,搜索起始port随时间增加也变大
参考资料
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002396411
linux中TCP的socket、bind、listen、connect和accept的实现
How Linux allows TCP introspection The inner workings of bind and listen on Linux.
https://idea.popcount.org/2014-04-03-bind-before-connect/
How to stop running out of ephemeral ports and start to love long-lived connections
connect() why you so slow?https://blog.cloudflare.com/linux-transport-protocol-port-selection-performance https://lpc.events/event/17/contributions/1593/attachments/1208/2472/lpc-2023-connect-why-you-so-slow.pdf?file=lpc-2023-connect-why-you-so-slow.pdf